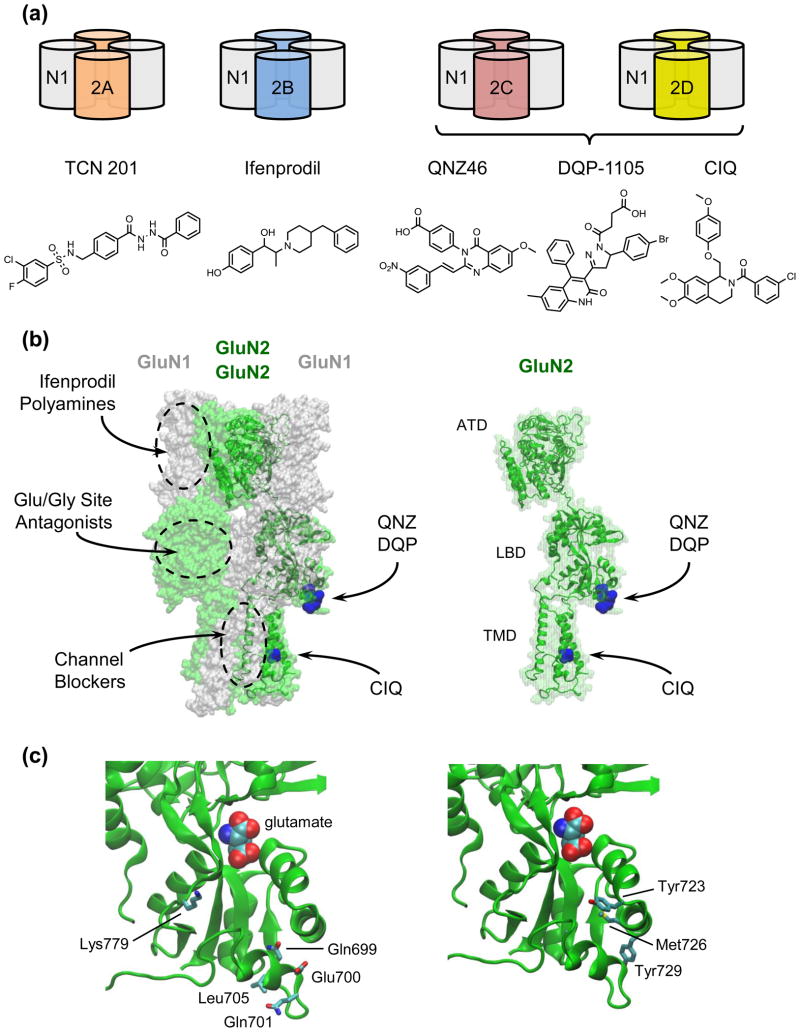
Figure 1. NMDA Receptor Architecture and Ligand Binding Sites.
NMDA receptors are tetrameric ion channels canonically comprised of two GluN1(labeled N1) subunits and two GluN2 subunits (2A, 2B, 2C, or 2D) in a 1-2-1-2 arrangement (a). Receptors containing different GluN1 splice variants and/or a GluN3 subunit have distinct functional properties. Additionally, much of the diversity among receptor subtypes arises from the GluN2 subunits, which are critical in determining biophysical and pharmacological properties of the receptor. Representative compounds acting with greater than 50-fold selectivity at individual GluN2-containing receptors are shown below the receptor subtypes. (b) Major ligand binding sites on the NMDA receptor are depicted on a GluN1/GluN2D homology model based on X-ray structures of a GluA2 tetramer (PDB 3KG2), GluN1 amino terminal domain (PDB 3Q41), GluN1 ligand binding domain (PDB 2A5T), GluN2B ATD (PDB 3JPY), and GluN2D LBD (PDB 3OEN) (Modeller 9.9). Ifenprodil and related GluN2B-selective molecules bind to the amino terminal domain (ATD) as do polyamines. Competitive antagonists of glycine and glutamate bind to the ligand binding domain (LBD) of GluN1 and GluN2, respectively. Channel blockers bind in the transmembrane domain (TMD). Residues critical for the activity of QNZ46, DQP1105, or CIQ are shown in blue. Right, an individual GluN2 subunit from a tetrameric complex is shown with the sites for QNZ46, DQP-1105, and CIQ highlighted in blue. (c) The lower portion of the GluN2D LBD harbors residues critical for the actions of QNZ46. Residues Gln699, Glu700, Gln701, Leu705 and Lys779 (left) are not conserved between GluN2D and GluN2A, while residues Tyr723, Met726, and Tyr729 (right) are conserved. Mutating Gln699, Glu700, Met726 and Tyr729 to the corresponding residue in GluN2A increased QNZ inhibition, while mutating Gln701, Leu705, Lys779, and Tyr729 to the corresponding GluN2A residue reduced QNZ inhibition.