Figure 3.
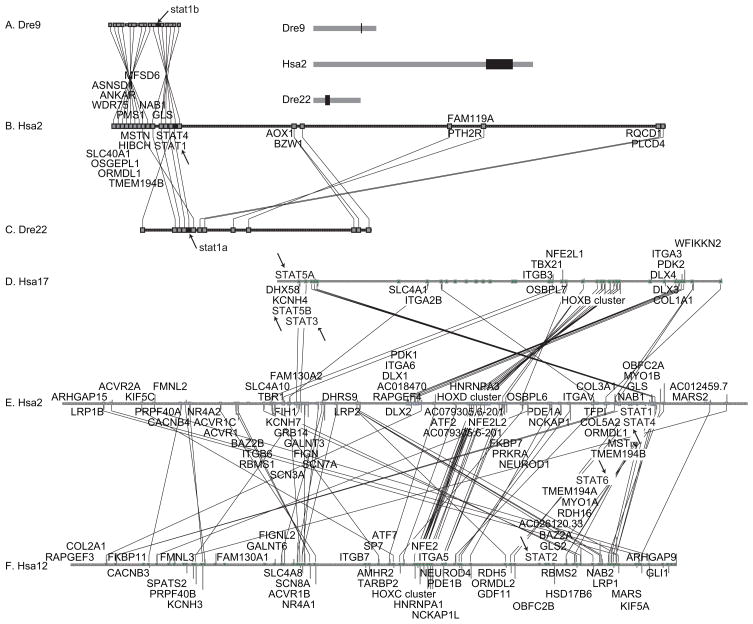
Conserved syntenies verify the history of the stat1 gene family. A. Conserved syntenies around zebrafish stat1b on zebrafish chromosome Dre9 were searched in the human genome using the Synteny Database (Catchen et al., 2009). B. Extensive conserved syntenies were found around STAT1 on human chromosome Hsa2. Lines between large boxes connect orthologs; small boxes represent genes without orthologs in the diagramed regions. C. Conserved syntenies around human STAT1 also appeared around zebrafish stat1a on Dre22. Chromosomal regions shown in black rectangles in the insert to the right of part A are blown up in parts A, B, and C. Arrows indicate the positions of stat genes. Note that on Hsa2 and Dre9 STAT1/stat1 and STAT4/stat4 reside adjacent to each other. Genes (indicated in the order: HUMAN gene, dre9 gene, dre22 gene): STAT4, stat4; STAT1, stat1b, stat1a; GLS, gls, gls; NAB1, NP_001116745.1, si:dkeyp-84a8.1; TMEM194B, B0UYT4; MFSD6, zgc:92925, si:dkey-188p4.2; HIBCH, hibch; MSTN, mstn, gdf8; PMS1, pms1; ORMDL1, ormdl1; OSGEPL1, osgepl1; ANKAR, ankar; slc40a1, slc40a1; WDR75, wdr75. The following genes are HUMAN, dre22gene: RQCD1, rqcd1; PLCD4, plcd4a; PTH2R, si:dkeyp-4h4.1; FAM119A, zgc:110528; FAM119A; AOX1, aox1; BZW1, bzw1a. D–F. Human STAT genes occupy paralogy groups that appear to have originated in the R1 and R2 rounds of genome duplication that preceded the vertebrate radiation. Human paralogs of genes residing in the 20 Mb region of Hsa2 surrounding STAT1 between 180 and 200 Mb were plotted on the rest of the human chromosomes with gene order according to the location on human chromosome 2 (Hsa2) using the Dotplot feature of the Synteny database (Catchen et al., 2009). Results showed that Hsa2 genes, including STAT1 and STAT4, showed extensive paralogy with Hsa12, which contains STAT2 and STAT6, with Hsa17, which contains STAT3, STAT5A and STAT5B (arrows), and with Hsa7, which lacks any STAT genes and is thus omitted from the figure, but has many other paralogs closely linked to STAT genes, e.g., potassium channel family H (KCNH2, 7q36.1; KCNH7, 2q24.2; KCNH3 12q13; KCNH4, 17q21.2), the HOX clusters (HOXA4, 7p15.2; HOXD4, 2q31.1; HOXC4, 12q13.3; HOXB4, 17q21.32), erythroid-derived nuclear factor-2 (NFE2L3, 7p15.2; NFE2L2, 2q31; NFE2, 12q13; NFE2L1, 17q21.3), and many other gene families.