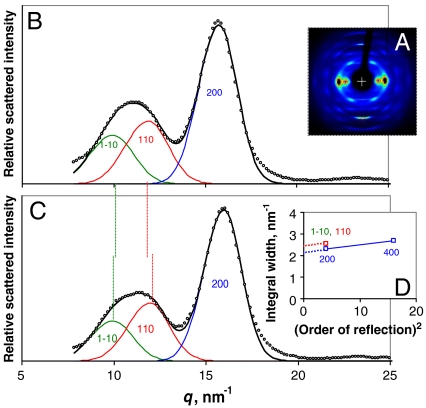
Fig. 2.
Wide-angle X-ray scattering from spruce wood. (A). WAXS pattern from dry spruce wood. (B). Background-corrected equatorial WAXS profiles from dry spruce wood with the 1–10, 110, and 200 reflections fitted by asymmetric functions, using the approximation that the widths of the overlapping 1–10 and 110 reflections were equal. (C). Background-corrected equatorial WAXS profiles from hydrated spruce wood, processed as (B). (D). Variation of the widths of the equatorial reflections with the square of the reflection order. The slope of the line connecting the widths of the 200 and 400 reflections depends on the mean value of the disorder factor and its intercept approximates to the disorder-corrected width. In the absence of measurable higher-order reflections the intercept was estimated for the 1–10 and 110 reflections using the same slope.