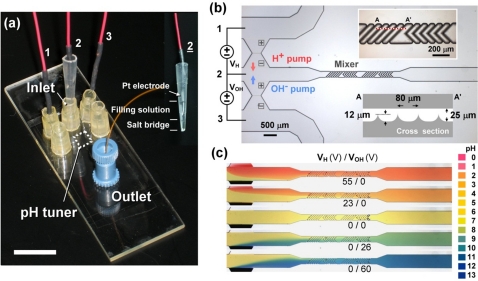
Figure 3.
(a) Bipolar membrane-based microfluidic pH tuner enables pH adjustment by separately controlling the voltage biases across two upstream bipolar membranes via three Pt electrodes in the reservoirs. In electrode 2, a salt-bridge is used to prevent direct contact with the sample solution. The inset shows the configuration of the salt-bridge electrode 2. Scale bar is 1 cm. (b) pH actuation in microfluidics with two sets of upstream bipolar membrane serving as proton and hydroxide ion pumps. The numbers in the circuit indicate the corresponding electrodes in (a). The insets show the zoom-in image and the illustrated cross-section (not in scale) of the mixer channel. (c) By adjusting the voltages VH and VOH, various pH conditions can be generated in microfluidic channels by mixing different fractions of protons or hydroxide ions under a flow rate of 2 μl∕min. The resulting pH values are estimated to be 3, 5, 7, 9 and 11 from top to bottom, according to the pH chart.