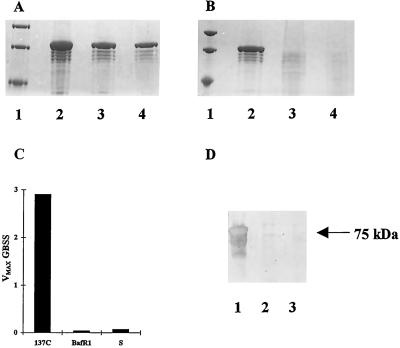
Figure 7.
Detection of GBSS activity and protein from starch-like granules of phytoglycogen-producing strains. A and B, Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 stained 5% to 7.5% SDS-acrylamide gels of starch-bound proteins. In A and B, lanes 1 display molecular-mass size standards (from top to bottom 94, 67, and 43 kD). A, Lane 4 represents starch-bound proteins extracted from 6 mg of polysaccharide purified from the wild-type strain 137C after nitrogen starvation. Lanes 2 and 3 display starch-bound proteins extracted from 6 and 3 mg, respectively, of starch purified from nitrogen-supplied wild-type cultures. The major 76-kD band corresponds to the GBSS protein and displays the typical GBSS N-terminal sequence (Delrue et al., 1992). B, Lane 2 represents starch-bound proteins extracted from 2 mg of starch purified from nitrogen-supplied wild-type cultures (strain 137C). Lanes 3 and 4 display starch-bound proteins extracted from two samples of starch purified, respectively, from nitrogen-supplied sta7–7::ARG7 (strain S) and sta2–29::ARG7 (strain BafR1). C, Histograms of GBSSI activity are expressed as nanomoles of ADP-Glc incorporated into glucan per minute and per milligram starch. Starch was extracted from nitrogen-starved algae. Strains BaFR1 and S contain gene disruptions inactivating GBSSI and DBE, respectively. 137C is the wild-type strain. D, Western blot of starch-bound proteins extracted from equal amounts of polysaccharide. Proteins cross-reacting with antibodies directed against the C-terminal consensus peptide sequence found on vascular plant starch synthases (see Methods) were selectively revealed. Lanes 1, 2, and 3, Strains 137C, BAFR1, and S, respectively.