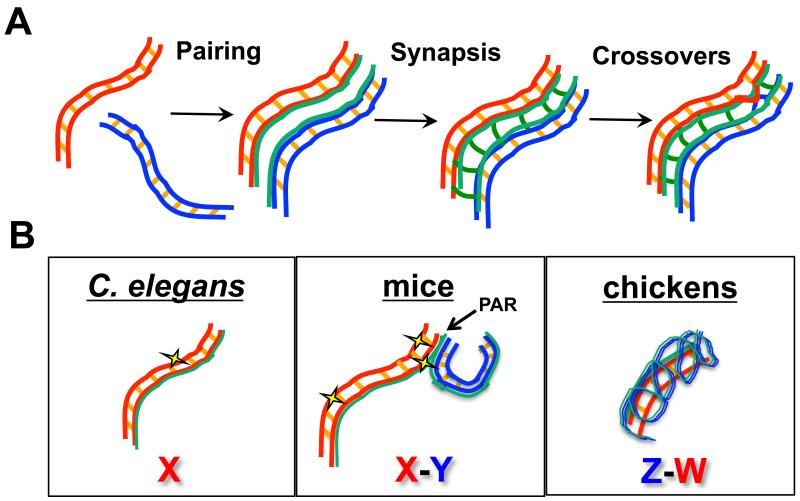
Figure 2.
Autosome and sex chromosome behavior in meiotic prophase. A) Major events in meiotic prophase are shown for homologous autosomes (red and blue). Duplicated sister chromatids are held together by sister chromatid cohesion (orange cross lines between sisters) and elaborate chromosomal axes (green) during the process of pairing, where homologous chromosomes align. During synapsis, the synaptonemal complex (green cross lines) stabilizes the aligned homologous chromosomes. In this context, crossover recombination occurs to allow for segregation of homologous chromosomes at the first meiotic division. B) Configuration of heteromorphic sex chromosomes in C. elegans, mice, and chickens in meiotic prophase. In worms, a single X chromosome lacks a partner but elaborates axial components and incurs DSBs (yellow star). In mice, the X and Y pair and synapse at the pseudoautosomal region (PAR), and DSBs are found along the length of the XY chromosomes but occur at a higher frequency at the PAR. In chickens, the larger Z chromosome synapses with the smaller, non-homologous W chromosome; at this stage no markers of DSBs are observed.