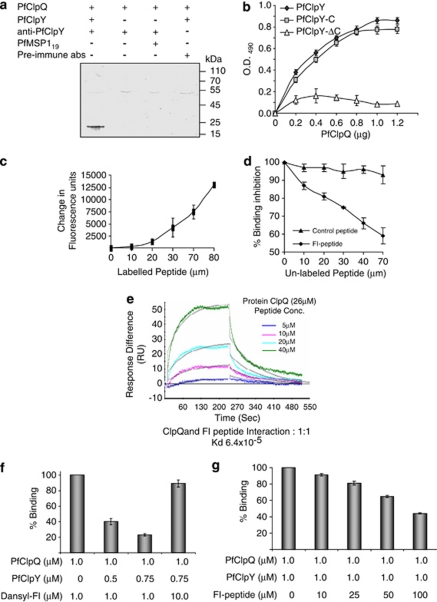
Figure 2.
(a and b) Interaction of PfClpQ with PfClpY and its C-terminal fragments. (a) Solution-binding assays of PfClpQ and PfClpY recombinant proteins followed by in vitro pulldown of the protein complex using anti-PfClpY antibodies; PfClpQ protein was detected in the pulled down protein complex by western blot analysis. Control reactions were carried out in the absence of PfClpY protein or replaced with a non-specific protein (PfMSP-119); in another reaction the anti-ClpY antibodies were replaced with control antibodies (pre-immune). (b) In vitro solid-phase interaction of PfClpQ with increasing concentration of PfClpY and its C-terminal fragments; protein–protein interaction was estimated by ELISA using anti-PfClpY antibody. The PfClpY and PfClpY-C showed concentration-dependent interaction with PfClpQ, whereas PfClpY-ΔC showed no significant binding. (c–e) Interaction of synthetic peptide corresponding to C terminus of PfClpY (FI-peptide) with PfClpQ protein. (c) A solution-binding assay of PfClpQ with Dansyl-labeled FI-peptide (Dansyl-FI), complex formation lead to change in fluorescence in the reaction. Fluorescence change (ΔF) was estimated using different concentration of the labeled peptide. The labeled peptide showed concentration-dependent binding with PfClpQ. (d) Inhibition of binding of Dansyl-FI and PfClpQ in presence of increasing concentration of unlabeled FI-peptide. Increasing concentration of unlabeled FI-peptide reduced binding of Dansyl-FI in a concentration-dependent manner. (e) Global fitting of the sensograms obtained by flowing increasing concentrations (5, 10, 20, 40 μM) of FI-peptide for 4 mins on PfCIpQ immobilized on the CM5 chip and dissociation for 4 min under similar flow conditions. Buffer alone was used as control that showed no responses to PfCIpQ. (f and g) FI-peptide and PfClpY shares the binding site on PfClpQ. (f) Percentage binding of FI-peptide and PfClpQ in a solution-binding assay in absence or presence of increasing concentration of PfClpY. Presence of PfClpY reduced the binding of FI-peptide and PfClpQ; a 10-fold increase in FI-peptide concentration restored the binding with PfClpQ. (g) Percentage binding of PfClpQ and PfClpY in a ELISA-based assay in absence or presence of increasing concentration of FI peptide