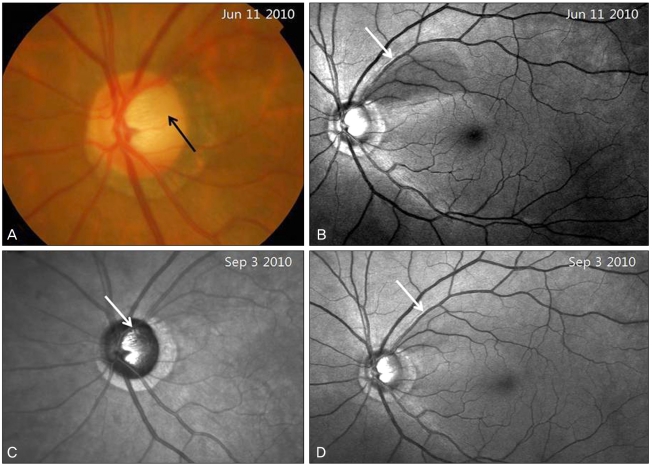
Fig. 1.
(A) Disc photography showing a round, gray, superotemporal optic disc pit (black arrow) in the left eye. (B) Red-free fundus photography. The superotemporal wedge-shaped retinal nerve fiber layer defect is shown (white arrow). (C) An infrared laser ophthalmoscope image shows the optic disc pit more clearly (white arrow). (D) After 3 months of a topical prostaglandin analogue medication, the retinal nerve fiber layer defect seems to have decreased (white arrow).