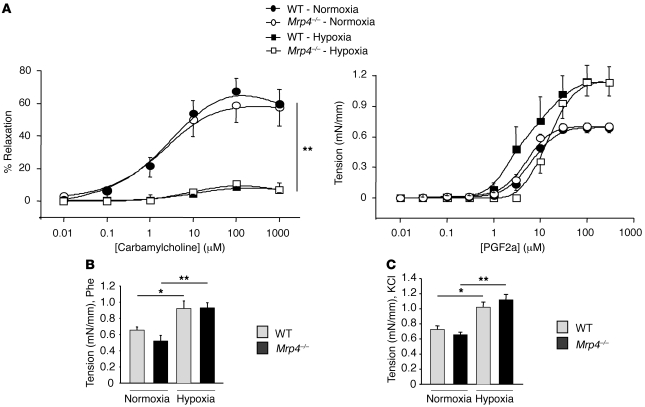
Figure 6. Relaxation and contraction of intrapulmonary arteries from WT and Mrp4–/– mice in normoxic or hypoxic conditions.
(A) Relaxation to carbamylcholine (0.01 to 1000 μM) in intrapulmonary arteries precontracted with either 10 μM or 30 μM of PGF2a in normoxic and chronic hypoxic mice, respectively (n = 8–13 rings, 4–5 mice and n = 10 rings, 6 mice, respectively). Relaxation is expressed as a percentage of the precontraction to PGF2a. Dose-dependent contraction to PGF2a (0.01 to 300 μM) (n = 8 rings, 3 mice in normoxia and n = 6 rings, 6 mice in chronic hypoxia) (**P < 0.001). (B) Comparison of the contraction to 10 μM phenylephrine (Phe) (n = 9–13 rings, 4–5 mice in normoxia and n = 16 rings, 6 mice in chronic hypoxia). (C) Comparison of the contraction to high potassium solutions (80 mM KCl) (n = 16 rings and 6 mice in normoxia and chronic hypoxia). (*P < 0.05).