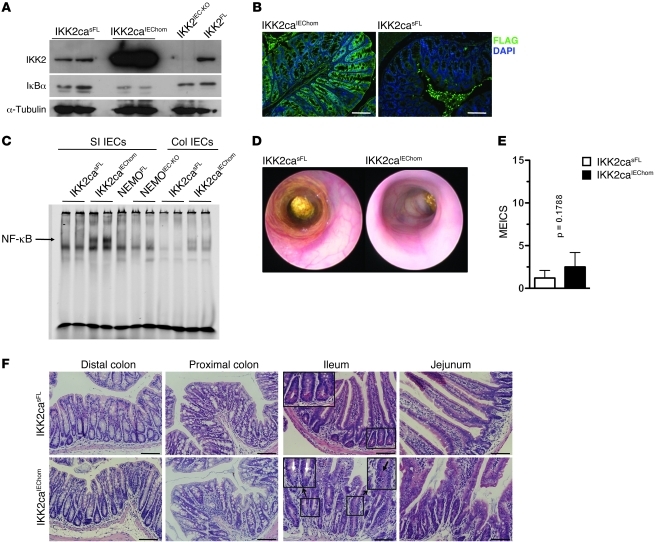
Figure 1. IKK2ca expression in IECs induces NF-κB activation and mild intestinal inflammation.
(A) Immunoblot reveals increased IKK2 expression and reduced levels of IκBα in SI IECs from IKK2caIEChom mice compared with IKK2casFL littermates. (B) Immunofluorescent staining with anti-FLAG antibodies shows IEC-specific expression of FLAG-IKK2ca in IKK2caIEChom colon sections. Background staining in the lumen of the IKK2casFL colon results from incomplete removal of luminal contents. (C) EMSA reveals increased NF-κB DNA-binding activity in nuclear extracts from IKK2caIEChom SI and colonic IECs. (D) Representative endoscopic images of colons from 8-week-old IKK2casFL and IKK2caIEChom mice. (E) Quantification of MEICS showing no significant colonic inflammation in 7- to 9-week-old IKK2caIEChom (n = 10) mice compared with IKK2casFL (n = 5) littermates. Data are presented as mean ± SD. (F) H&E-stained sections show crypt elongation and increased immune cell infiltration in the SI and colon of IKK2caIEChom compared with IKK2casFL mice. Note the lack of Paneth cells in ileal crypts in IKK2caIEChom mice (indicated by white arrows in inset). The black arrow indicates a mislocalized Paneth cell. Scale bars: 50 μm.