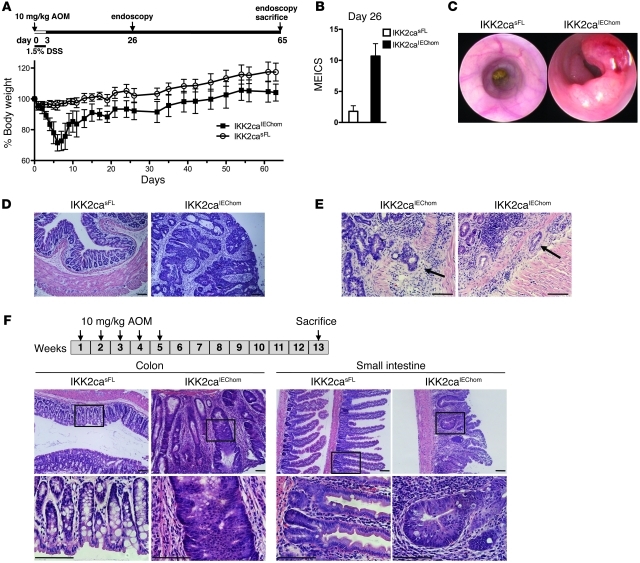
Figure 4. IKK2caIEChom mice display strongly enhanced tumorigenesis in response to AOM treatments.
(A) IKK2caIEChom and IKK2casFL mice were injected with 10 mg/kg AOM and given 1.5% DSS in drinking water for 3 days followed by regular drinking water (n ≥ 9 per genotype; data shown as mean ± SD). (B) MEICS determined on day 26 revealed severe colon inflammation in IKK2caIEChom but not in IKK2casFL mice (n ≥ 6 per genotype; data shown as mean ± SD). (C) Endoscopic analysis on day 65 revealed pronounced tumor formation in the distal colons of IKK2caIEChom but not in IKK2casFL mice. (D) Histological analysis of colon cross sections revealed the presence of advanced adenomas showing loss of epithelial cell differentiation and epithelial stratification in IKK2caIEChom mice. In contrast, the colonic mucosa of IKK2casFL mice appeared normal. (E) Histological tissue sections from AOM/DSS-treated IKK2caIEChom mice showing colonic adenocarcinomas as identified by invasion of epithelial tissue into the submucosa (indicated by arrows). (F) IKK2caIEChom and IKK2casFL mice (n ≥ 8) received 5 weekly injections of 10 mg/kg AOM and were sacrificed 13 weeks after the first injection. Histological cross sections revealed the presence of tumors displaying pronounced epithelial hyperplasia and early dysplastic lesions in both colon and SI of IKK2caIEChom but not IKK2casFL mice. Scale bars: 50 μm.