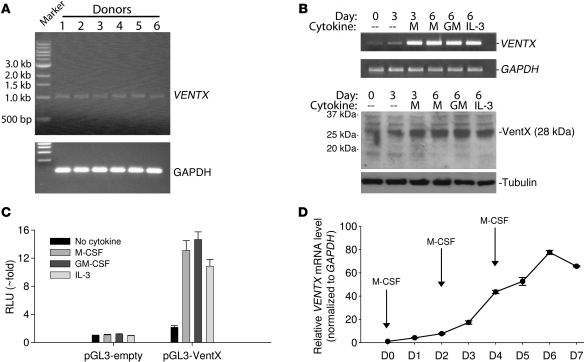
Figure 1. Upregulation of VentX expression during monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation.
(A) VentX expression in circulating monocytes. Monocytes were magnetically isolated by anti-CD14 beads from peripheral blood of healthy adult donors. Total RNA was extracted, and RT-PCR analysis of VENTX mRNA level was conducted as described in Methods. (B) VentX expression during monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation in vitro. Monocytes were cultured in the presence of M-CSF (M), GM-CSF (GM), or IL-3 for the indicated days or in the absence of cytokines for 3 days. Upper panel: VENTX mRNA levels were determined by RT-PCR. Lower panel: VentX protein levels were determined by Western blot analysis, using VentX-specific antibodies. VentX expression in freshly isolated monocytes was used as baseline control (Day 0). (C) Induction of VENTX promoter activity by the indicated cytokines. Freshly isolated monocytes were electroporated with pGL3-VentX promoter luciferase reporter construct or a control empty pGL3 luciferase reporter. Twenty-four hours after electroporation, cells were treated with the indicated cytokines for an additional 24 hours. Cell lysates were then obtained, and luciferase activity was measured. Data represent mean + SD of triplicates of 1 representative experiment. (D) Time course of VentX expression during in vitro induction of monocyte differentiation into macrophages. Monocytes were subjected to M-CSF treatment in vitro for the indicated time. The VENTX mRNA levels were determined by quantitative PCR for up to 7 days.