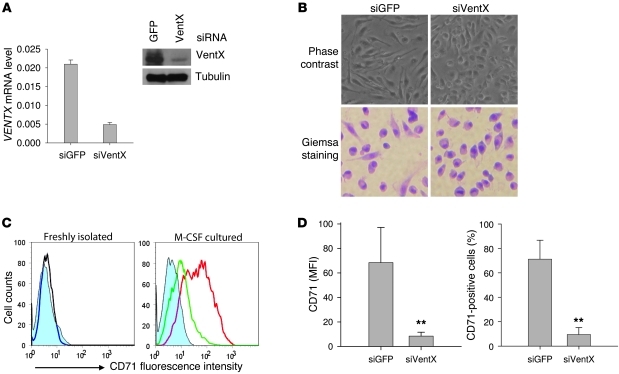
Figure 2. Knockdown of VENTX compromises the macrophage differentiation of primary monocytes.
(A) Knockdown of VENTX expression in primary monocytes by RNA interference. Monocytes were transfected with siRNA against GFP or VentX through electroporation. VENTX mRNA levels were determined by real-time PCR at 3 days after transfection (left); VentX protein level was determined by Western blotting at 4 days after transfection (right). (B) Effects of VENTX knockdown on macrophage morphogenesis during M-CSF–induced differentiation. Monocytes were transfected with either siGFP or siVentX and subsequently exposed to 100 ng/ml M-CSF. At 4 days after transfection, the morphology of macrophages was revealed by phase contrast microscopy (upper panel) and Wright-Giemsa staining (lower panel). Original magnification, ×200. Note: A portion of cells lost their original morphology during the Wright-Giemsa staining procedure. (C) Effects of VENTX knockdown on macrophage surface expression of CD71. Left panel: CD71 expression was not detected on cell surface of freshly isolated monocytes. Right panel: CD71 expression on M-CSF–treated monocytes at 4 days after siRNA transfection. Filled blue histogram represents the isotope control staining; red histogram represents monocytes transfected with siGFP; green histogram represents monocytes transfected with siVentX. (D) Bar graphs show mean + SD of 6 different experiments in C. Paired t test was used to reveal statistical significance. **P < 0.01.