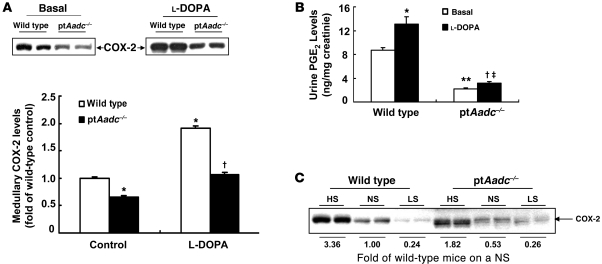
Figure 6. Renal medullary COX-2 was inhibited in ptAadc–/– mice.
(A) Renal medullary COX-2 levels were lower in ptAadc–/– mice than wild-type mice, with or without l-DOPA stimulation (*P < 0.01 vs. basal wild type, †P < 0.001 vs. l-DOPA treated wild type; n = 4 in each group). (B) Urinary PGE2 levels were significantly lower in ptAadc–/– mice than wild-type mice, with or without l-DOPA stimulation (*P < 0.05 vs. basal wild type, **P < 0.01 vs. basal wild type, †P < 0.05 vs. basal ptAadc–/–, ‡P < 0.005 vs. l-DOPA–treated wild type; n = 4 in each group). (C) High-salt diet–induced (HS-induced) renal medullary COX-2 elevations were attenuated in ptAadc–/– mice. Also shown is densitometric quantification of COX-2 immunoreactive protein in response to alterations of dietary salt intake represented as fold of expression of wild-type mice on a normal-salt diet (NS). LS, low-salt diet.