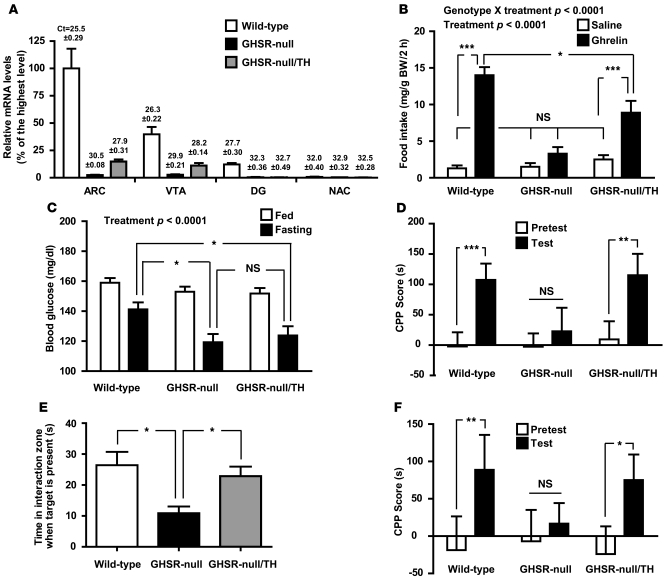
Figure 3. Selective GHSR expression in catecholaminergic neurons is sufficient for several ghrelin-mediated actions.
(A) Cre-mediated restoration of Ghsr mRNA expression is observed in brain regions of GHSR-null/TH mice containing catecholaminergic neurons programmed to express GHSRs, including the ARC and VTA, as determined using qRT-PCR (n = 6 per group). Mean ± SEM threshold cycle values for Ghsr mRNA in each brain site are denoted above the bars. (B) Ghrelin-induced acute food intake is partially restored in GHSR-null/TH mice. (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.0001) (C) Fasting blood glucose levels are not restored to wild-type levels in GHSR-null/TH mice (*P < 0.05). (D) Administered ghrelin-induced CPP for HFD (**P < 0.005, ***P < 0.0001), (E) social interaction phenotype after CSDS (*P < 0.05), and (F) CSDS-induced CPP for HFD (*P = 0.042, **P = 0.020) are all restored to wild-type levels in GHSR-null/TH mice. For B–F, n = 19–30 wild-type mice (including 12–22 mice without and 5–14 mice with TH-cre), n = 14–34 GHSR-null mice, and n = 14–23 GHSR-null/TH mice. Significant effects of treatment (ghrelin vs. saline or ad libitum–fed versus 24-hour fast) and significant genotype X treatment interactions are indicated.