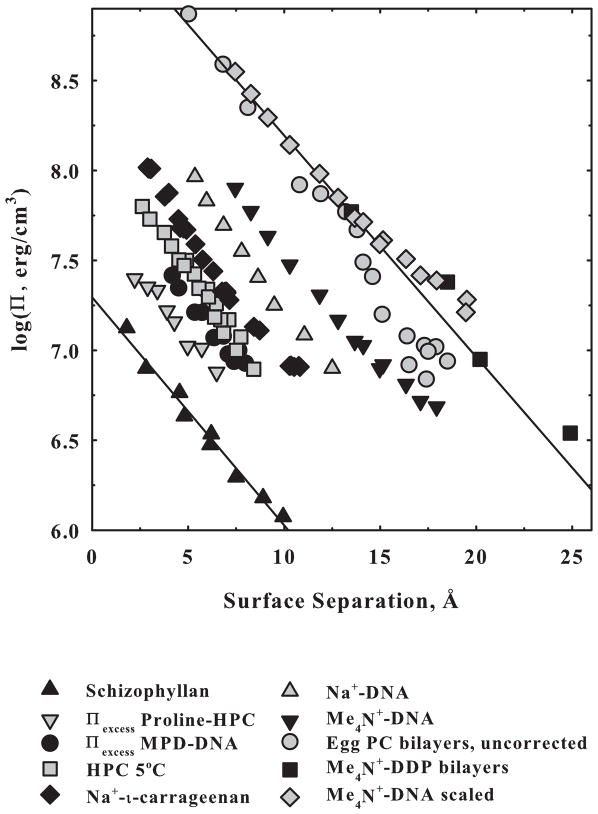
Figure 1.
A comparison of forces measured for several different systems in ordered arrays. Π is the osmotic pressure applied by the excluded polymer in the bulk solution acting on the condensed macromolecular phase. Distances are given as approximate surface-to-surface separations of macromolecules. Schizophyllan [55] and hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) [30] are completely uncharged. DNA in NaBr and TMABr, tetramethyl ammonium, (unpublished data) and ι-carrageenan in NaCl (unpublished data) are highly charged linear double helices. DDP (didodecyl phosphate) in TMA+ salt is a highly charged planar bilayer (data from [56]). Egg PC is a zwitterionic planar bilayer that has the phosphate and quaternary amine of the head group covalently linked (data from [57]). The TMA+-DNA force has also been corrected to planar packing and to the same surface area/phosphate as DDP. The close overlap of the corrected TMA+-DNA, egg PC (that has about the same surface area/molecule as DDP) and TMA+-DDP forces illustrates the striking similarity of these homologous systems. The salt concentrations for the charged surfaces are high enough that forces are insensitive to ionic strength. The excess pressures due to solute exclusion are also shown for the nonpolar alcohol methylpentane diol (MPD) at 1 molal interacting with DNA and for zwitterionic proline at 1 molal interacting with uncharged HPC. The straight lines show a decay length of ~4 Å. The force amplitudes span a range greater than 100-fold.