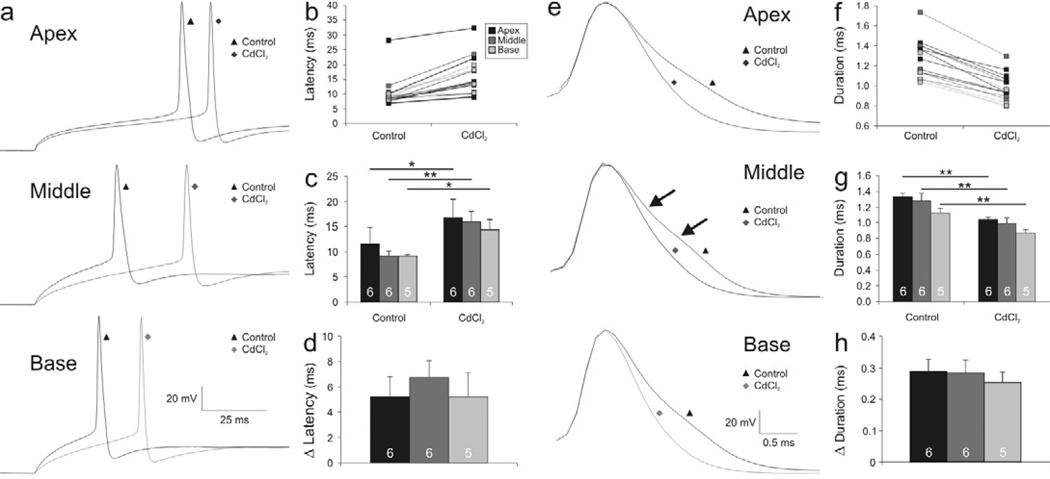
Figure 4.
Action potential latency and duration are prolonged differentially in apical, middle, and basal neurons after CdCl2 application. (a) Representative whole-cell current clamp traces from apical, middle, and basal neurons exemplifying action potential latency at threshold before (black traces labeled with triangles) and after application of CdCl2 (gray traces labeled with diamonds). (b) Individual latency measurements before and after CdCl2 exposure. (c) Averaged measurements show significant increases in action potential latency for apex, middle, and base neuronal recordings after CdCl2 application. (d) Change in latency before and after the CdCl2 application. (e) Representative traces aligned at peak action potential voltage exemplifying action potential duration differences of apical, middle, and basal recordings before (black traces labeled with triangles) and after application of CdCl2 (gray traces labeled with diamonds). (f) Individual duration measurement before and after CdCl2 application. (g) Averaged measurements show significant differences in action potential duration for recordings made from apex, middle, and basal neurons exposed to CdCl2. (h) Change in duration before and after CdCl2 application.