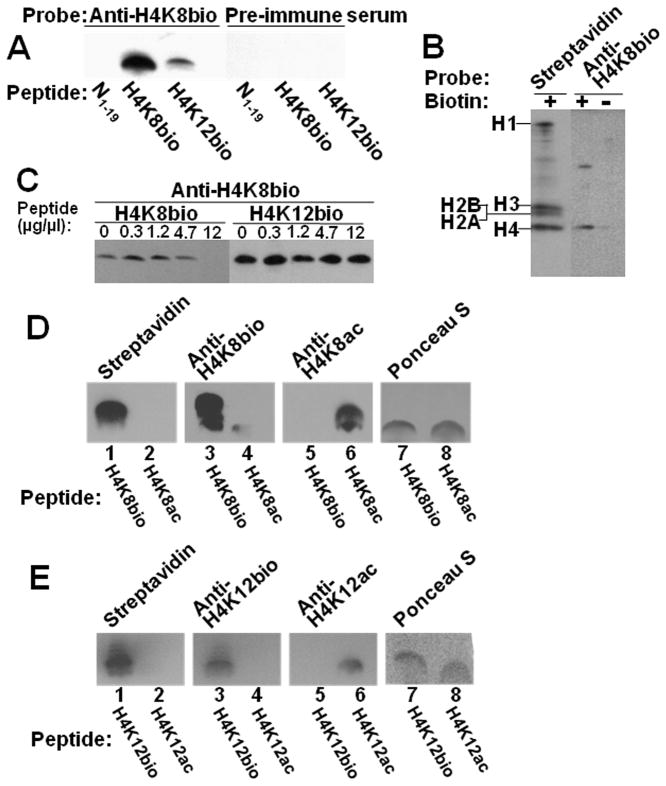
Fig. 4. Specificity of antibodies to H4K8bio and H4K12bio.
Panel A: Transblots of peptides N1–19 (non-biotinylated negative control), H4K8bio, and H4K12bio were probed with anti-H4K8bio; pre-immune serum was used as negative control. Panel B: HCl extracts of histones from Jurkat cells were probed using streptavidin and anti-H4K8bio; samples of biotin-free histones (“-”) were generated by using avidin agarose. Panel C: HCl extracts of histones from Jurkat cells were probed with anti-H4K8bio after pre-incubation of antibodies with increasing amounts of competing peptides H4K8bio and H4K12bio; controls (“C”) were prepared without peptide competitors. For some gels, bands from the same analytical runs were electronically rearranged to facilitate comparisons. Panel D: Peptides H4K8bio and H4K8ac were probed with streptavidin (lanes 1 and 2), anti-H4K8bio (lanes 3 and 4) and anti-H4K8ac (lanes 5 and 6); Ponceau S was used as loading control (lanes 7 and 8). Panel E: Peptides H4K12bio and H4K12ac were probed with streptavidin (lanes 1 and 2), anti-H4K12bio (lanes 3 and 4) and anti-H4K12ac (lanes 5 and 6); Ponceau S was used as loading control (lanes 7 and 8).