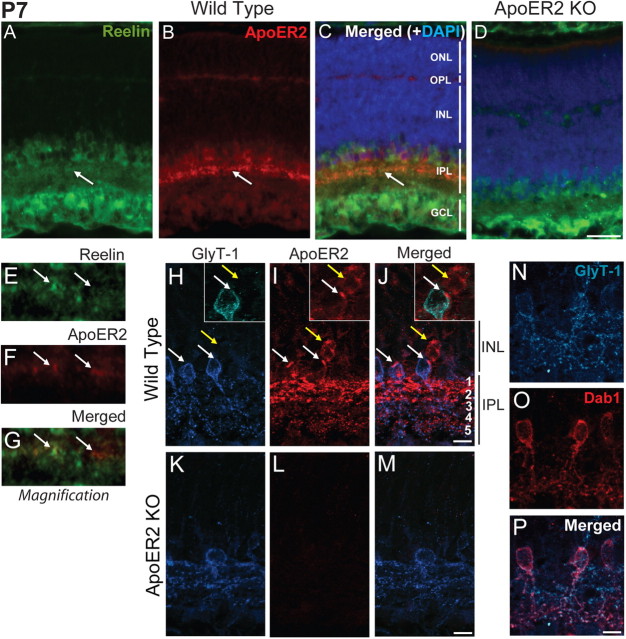
Figure 2.
Localization of ApoER2 in the retina at P7. A–D, P7 retinas from wild-type (A–C) and ApoER2 KO mice (D) were immunostained for ApoER2 (red) and Reelin (green). They were also colabeled with DAPI (blue) to indicate nuclear layers. Reelin was highly expressed by bipolar, amacrine, and ganglion cells and enriched in the IPL. ApoER2 was prominently expressed by a subset of cells residing within the INL and in their projections in the IPL. ApoER2 was also expressed in the OPL and faintly throughout the INL. ApoER2 and Reelin colocalized in the IPL (A–C, arrows). D, Similar expression of Reelin was detected in ApoER2 KOs, but ApoER2 could not be detected. E–G, A 10 μm segment of the ApoER2/Reelin-positive stratum identified in A–C by arrows is magnified. Two colocalizing clusters of synapses are indicated with arrows. H–J, ApoER2 and GlyT-1 colocalized in cells alongside the IPL (white arrows), while ApoER2 was also detected in GlyT-1-negative cells (yellow arrows). In the IPL, ApoER2 was most abundant in s1–s2 (OFF strata), where it also partially colocalized with GlyT-1. ApoER2 was also sparsely detected and colocalized with GlyT-1 in s3–s5 (ON strata). K–M, ApoER2 KOs had altered distribution of GlyT-1 and no specific ApoER2 signal. The identity of A-II amacrine cells was confirmed by colocalization of GlyT-1 (blue) and Dab1 (red). Scale bars: D (for A–D) 30 μm; J (for H–J), M (for K–M), P (for N–P) 5 μm.