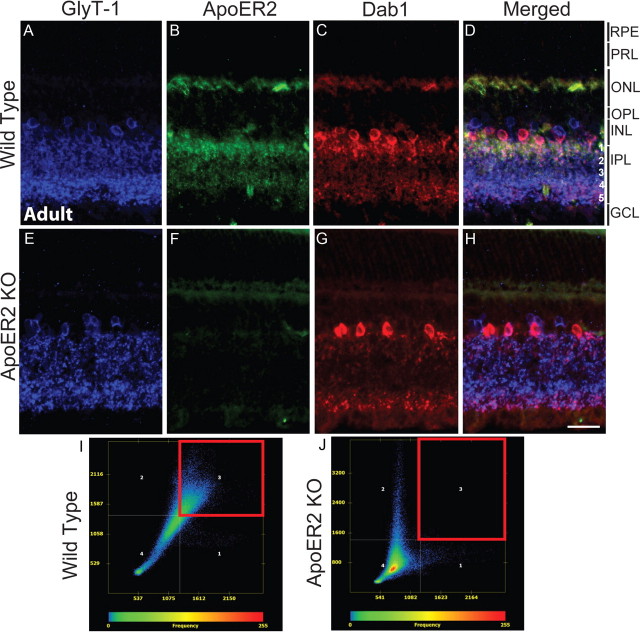
Figure 3.
Expression of ApoER2 in the mature retina. A–H, The expression of GlyT-1 (blue), ApoER2 (green), and Dab1 (red) was determined in the mature wild-type (A–D) and ApoER2 KO (E–H) retina. In both, glycinergic amacrine cells formed two strata of synapses in the IPL, which comprise s1–s2 (OFF sublamina) and s3–s5 (ON sublamina) (A, E). ApoER2 was expressed predominantly in s1–s2, but could also be detected in s3–s5, the INL, and OPL (B). ApoER2 could not be detected in KOs (F). Some tissue autofluorescence is evident, particularly in photoreceptor segments. C, G, Dab1 was expressed by A-II amacrine cells in both wild-type and ApoER2 KO retinas, though A-II amacrine morphology was perturbed in KO retinas. Colocalization between Dab1, ApoER2, and GlyT-1 was evident in wild-type retinas (D) and analyzed using the Axiovision colocalization software module. I, J, Colocalization scatter plots were generated with the threshold established by eliminating background colocalization in ApoER2 KOs. Only the INL and IPL were included for analysis. Colocalized pixels gated in the red box reveal significant colocalization between ApoER2 and Dab1 in wild-type retinas (I) but not in ApoER2 KOs (J). Scale bar: H (for A–H), 30 μm.