Figure 1.
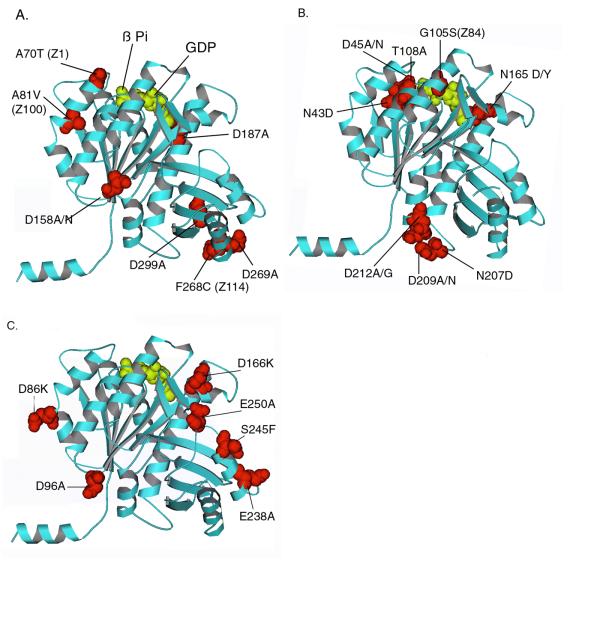
Mapping mutants on the atomic structure of Methanococcus FtsZ [8]. (A) Benign mutations; (B) GTP-contact mutations; (C) Lateral mutations. The amino acid numbers refer to the E. coli sequence, which were mapped to the corresponding amino acid in the Methanococcus sequence. Note that all of these amino acids are conserved in these two sequences as well as in most other FtsZ. Mutants identified in genetic screens are also indicated by their previous name (Z1, Z84). The subunits are oriented as they should be in a protofilament, based on the structure of tubulin viewed from outside the microtubule [9].
