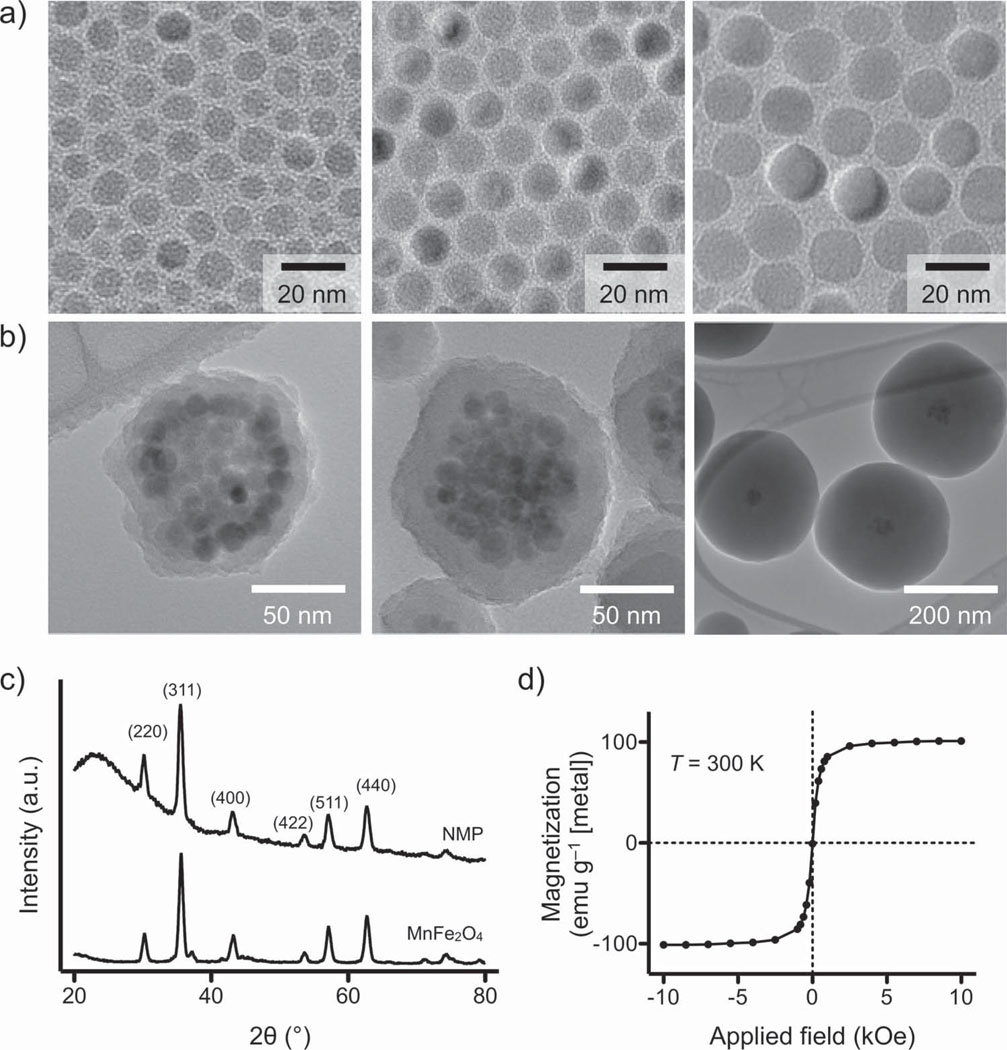
Figure 1.
Synthesis and characterization of NMP. a) Mn-doped ferrite crystals were prepared as core MNPs. These core particles were enlarged up to a diameter of 16 nm through seed-mediated growth. All Mn-MNPs had a narrow size distribution and consisted of a single domain. b) NMPs of different sizes were synthesized by encapsulating a cluster of Mn-MNPs (diameter 16 nm) within a silica shell of varying thickness. The estimated number of core Mn-MNPs per NMP was =57. While keeping the same cluster size, the shell thickness was varied from 9 to 140 nm. c) XRD demonstrated that NMPs exhibited identical peak patterns to their unmodified core Mn-MNPs; this confirmed that the cores are preserved during the silica-coating step. The broad background in NMP signal is due to the amorphous nature of the silica shell. d) At T = 300 K, NMPs are superparamagnetic and their saturation magnetization (100 emu g−1 [metal]) is similar to that of 16 nm Mn-MNPs (101 emu g−1 [metal]).