Fig. 5.
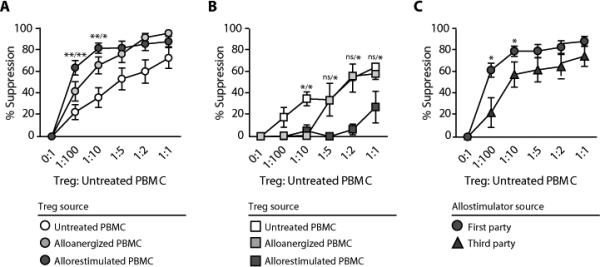
Suppression by CD4+ Treg cells after in vitro alloanergization and allorestimulation of PBMCs. (A) Mean percentage suppression (± SD) of first-party stimulated alloproliferation of untreated autologous responder PBMCs by CD4+ Treg cells from untreated, alloanergized, and allorestimulated alloanergized PBMCs. Data are for 12 HLA-mismatched stimulator- responder pairs. *P < 0.05; **P <0.01 [two-tailed paired t test com- paring suppression of first-party stimulated alloproliferation by CD4+ Treg cells from allorestimulated alloanergized PBMCs with CD4+ Treg cells from untreated (left) or alloanergized (right) PBMCs]. (B) Mean percentage suppression (± SD) of cytomegalovirus- specific proliferation of untreated autologous responder PBMCs by CD4+ Treg cells purified from untreated, alloanergized, and allorestimulated alloanergized PBMCs. Data are for three different HLA-mismatched stimulator- responder pairs. *P < 0.05 [two-tailed paired t test comparing suppression of cytomegalovirus proliferation by CD4+ Treg cells from untreated PBMCs with CD4+ Treg cells from alloanergized (left) or alloanergized allorestimulated (right) PBMCs]. ns, not significant. (C) Mean percentage suppression (± SD) of first- and third-party stimulated alloproliferation of untreated autologous responder PBMCs by CD4+ Treg cells purified from allorestimulated alloanergized PBMCs. Data are for 12 HLA-mismatched stimulator-responder pairs. *P < 0.05 (two-tailed paired t test comparing suppression of first-party stimulated alloproliferation with third-party stimulated alloproliferation).
