Figure 1.
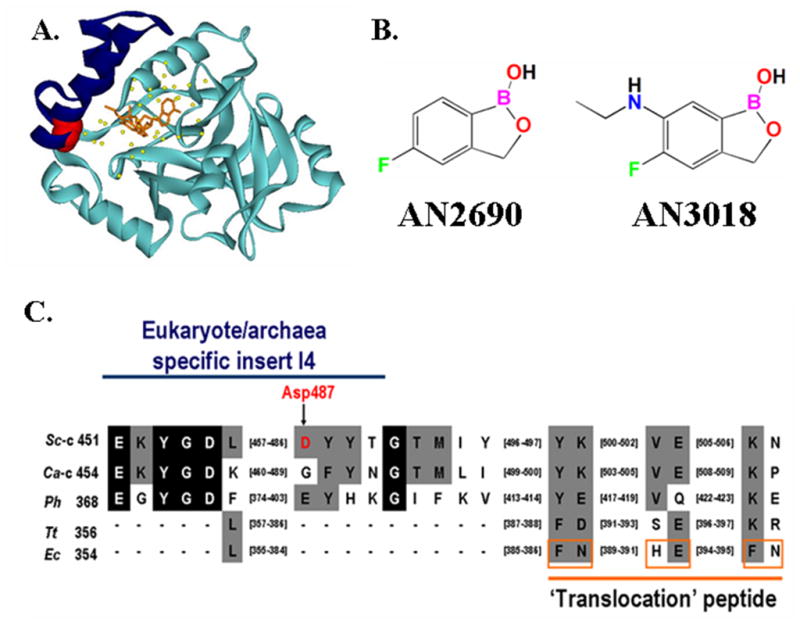
Primary and tertiary structures of LeuRS I4 ‘cap’ insert within the CP1 editing domain. (A) Crystal structure of Candida albicans cytoplasmic LeuRS CP1 domain in complex with AN3018-AMP (orange) (PDB entry 2WFG) [9]. The I4 insert (Glu454 to Asn493 in Candida albicans) is highlighted in blue with Gly490 (which corresponds to the Asp487 in yeast cytoplasmic LeuRS) shown in red. Yellow balls denote ordered water molecules in the editing pocket. (B) Chemical structures of AN2690 and AN3018. (C) Multiple sequence alignment of the I4 insert within the LeuRS CP1 domain. The blue line highlights the I4 insert. The Asp487 in yeast LeuRS is indicated in red and by the arrow. The orange line indicates the putative ‘translocation’ peptide proposed in Escherichia coli LeuRS [14]. The residues boxed in orange within this peptide are proposed to impair translocation. Abbreviations are: Thermus thermophilus (Tt), E. coli (Ec), S. cerevisiae cytoplasmic (Sc-c), C. albicans cytoplasmic (Ca-c) and P. horikoshii (Ph).
