Abstract
In the present study we have examined the effects of allopurinol and oxipurinol on the de novo synthesis of purines in cultured human fibroblasts. Allopurinol inhibits de novo purine synthesis in the absence of xanthine oxidase. Inhibition at lower concentrations of the drug requires the presence of hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase as it does in vivo. Although this suggests that the inhibitory effect of allopurinol at least at the lower concentrations tested is a consequence of its conversion to the ribonucleotide form in human cells, the nucleotide derivative could not be demonstrated. Several possible indirect consequences of such a conversion were also sought. There was no evidence that allopurinol was further utilized in the synthesis of nucleic acids in these cultured human cells and no effect of either allopurinol or oxipurinol on the long-term survival of human cells in vitro could be demonstrated.
At higher concentrations, both allopurinol and oxipurinol inhibit the early steps of de novo purine synthesis in the absence of either xanthine oxidase or hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. This indicates that at higher drug concentrations, inhibition is occurring by some mechanism other than those previously postulated.
Full text
PDF
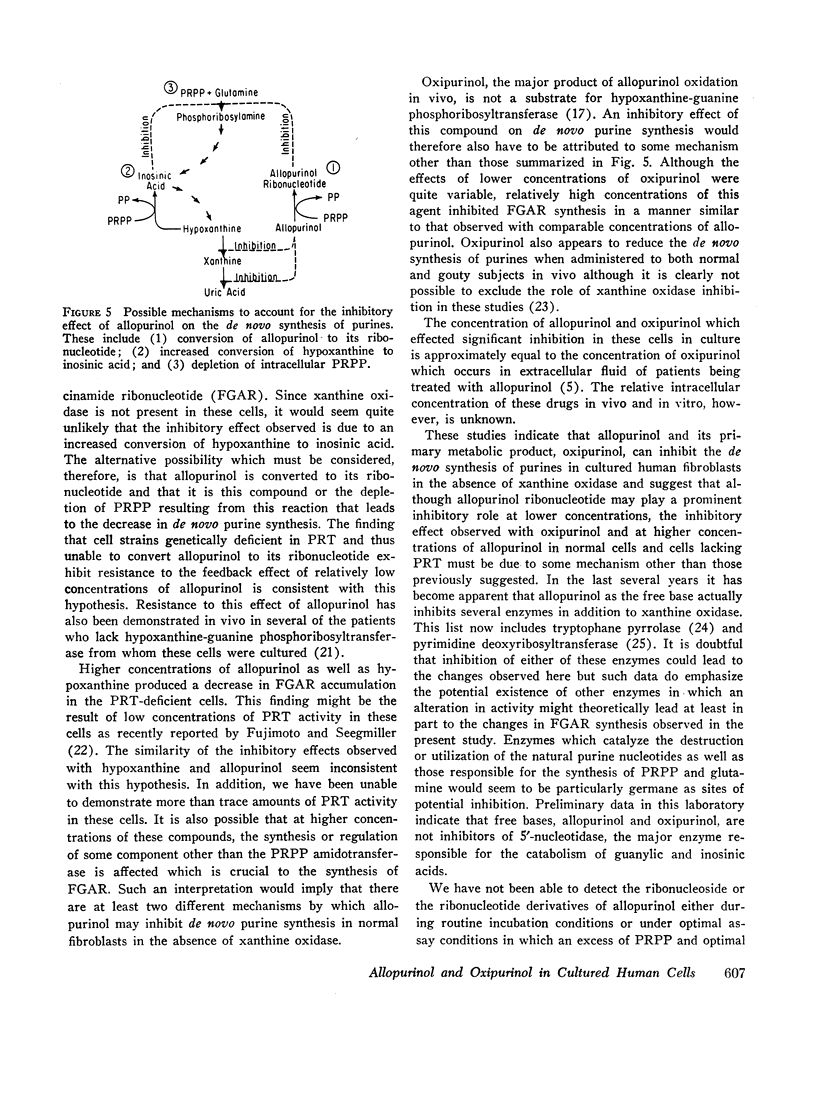


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becking G. C., Johnson W. J. The inhibition of tryptophan pyrrolase by allopurinol, an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. Can J Biochem. 1967 Nov;45(11):1667–1672. doi: 10.1139/o67-197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASKEY C. T., ASHTON D. M., WYNGAARDEN J. B. THE ENZYMOLOGY OF FEEDBACK INHIBITION OF GLUTAMINE PHOSPHORIBOSYLPYROPHOSPHATE AMIDOTRANSFERASE BY PURINE RIBONUCLEOTIDES. J Biol Chem. 1964 Aug;239:2570–2579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers R. A., Krömer H., Scott J. T., Watts R. W. A comparative study of the xanthine oxidase inhibitors allopurinol and oxipurinol in man. Clin Sci. 1968 Oct;35(2):353–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENGELMAN K., WATTS R. W., KLINENBERG J. R., SJOERDSMA A., SEEGMILLER J. E. CLINICAL, PHYSIOLOGICAL AND BIOCHEMICAL STUDIES OF A PATIENT WITH XANTHINURIA AND PHEOCHROMOCYTOMA. Am J Med. 1964 Dec;37:839–861. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90128-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion G. B. Enzymatic and metabolic studies with allopurinol. Ann Rheum Dis. 1966 Nov;25(6 Suppl):608–614. doi: 10.1136/ard.25.suppl_6.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion G. B., Kovensky A., Hitchings G. H. Metabolic studies of allopurinol, an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1966 Jul;15(7):863–880. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(66)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elion G. B., Yü T. F., Gutman A. B., Hitchings G. H. Renal clearance of oxipurinol, the chief metabolite of allopurinol. Am J Med. 1968 Jul;45(1):69–77. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEIGELSON P., DAVIDSON J. D., ROBINS R. K. Pyrazolopyrimidines as inhibitors and substrates of xanthine oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1957 Jun;226(2):993–1000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo R. C., Perry S., Breitman T. R. Inhibition of human leukocyte pyrimidine deoxynucleoside synthesis by allopurinol and 6-mercaptopurine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Oct;17(10):2185–2191. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLINENBERG J. R., GOLDFINGER S. E., SEEGMILLER J. E. THE EFFECTIVENESS OF THE XANTHINE OXIDASE INHIBITOR ALLOPURINOL IN THE TREATMENT OF GOUT. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Apr;62:639–647. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-62-4-639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAKOFF I. H., MEYER R. L. PREVENTION OF HYPERURICEMIA IN LEUKEMIA AND LYMPHOMA: USE OF ALOPURINOL, A XANTHINE OXIDASE INHIBITOR. JAMA. 1965 Jul 5;193:1–6. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03090010007001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley W. N., Rosenbloom F. M., Miller J., Seegmiller J. E. An enzymatic basis for variation in response to allopurinol. Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1968 Feb 8;278(6):287–293. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196802082780601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenitsky T. A., Elion G. B., Strelitz R. A., Hitchings G. H. Ribonucleosides of allopurinol and oxoallopurinol. Isolation from human urine, enzymatic synthesis, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 10;242(11):2675–2682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krenitsky T. A., Papaioannou R., Elion G. B. Human hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase. I. Purification, properties, and specificity. J Biol Chem. 1969 Mar 10;244(5):1263–1270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCCOLLISTER R. J., GILBERT W. R., Jr, ASHTON D. M., WYNGAARDEN J. B. PSEUDOFEEDBACK INHIBITION OF PURINE SYNTHESIS BY 6-MERCAPTOPURINE RIBONUCLEOTIDE AND OTHER PURINE ANALOGUES. J Biol Chem. 1964 May;239:1560–1563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POMALES R., BIEBER S., FRIEDMAN R., HITCHINGS G. H. Augmentation of the incorporation of hypoxanthine into nucleic acids by the administration of an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 28;72:119–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POMALES R., ELION G. B., HITCHINGS G. H. XANTHINE AS A PRECURSOR OF NUCLEIC ACID PURINES IN THE MOUSE. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Mar 15;95:505–506. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(65)90196-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbloom F. M., Henderson J. F., Caldwell I. C., Kelley W. N., Seegmiller J. E. Biochemical bases of accelerated purine biosynthesis de novo in human fibroblasts lacking hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1968 Mar 25;243(6):1166–1173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundles R. W. Metabolic effects of allopurinol and allo-xanthine. Ann Rheum Dis. 1966 Nov;25(6 Suppl):615–620. doi: 10.1136/ard.25.suppl_6.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundles R. W., Metz E. N., Silberman H. R. Allopurinol in the treatment of gout. Ann Intern Med. 1966 Feb;64(2):229–258. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-64-2-229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATTS R. W., ENGELMAN K., KLINENBERG J. R., SEEGMILLER J. E., SJOERDSMA A. ENZYME DEFECT IN A CASE OF XANTHINURIA. Nature. 1964 Jan 25;201:395–396. doi: 10.1038/201395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YUE T. F., GUTMAN A. B. EFFECT OF ALLOPURINOL (4-HYDROXYPYRAZOLO-(3,4-D)PYRIMIDINE) ON SERUM AND URINARY URIC ACID IN PRIMARY AND SECONDARY GOUT. Am J Med. 1964 Dec;37:885–898. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


