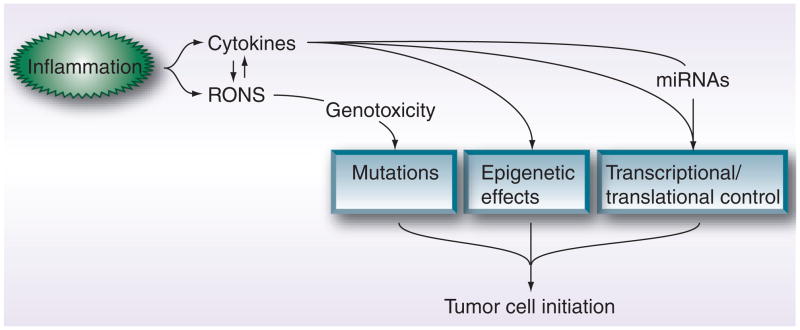
Figure 2. Chronic inflammation drives tumor cell initiation through direct mutational and indirect molecular effects.
Cytokines such as IL-6 promote cell transformation by modifying gene expression profiles, through mechanisms that include epigenetic effects and transcriptional factor control, as well as inducing protumorigenic miRNAs. RONS, on the other hand, serve to directly instigate gene mutations by damaging DNA and RNA. Interestingly, a positive feedback loop appears to exist between the ability of inflammatory cytokines to induce the synthesis of RONS and vice versa.
RONS: Reactive oxygen/nitrogen species.