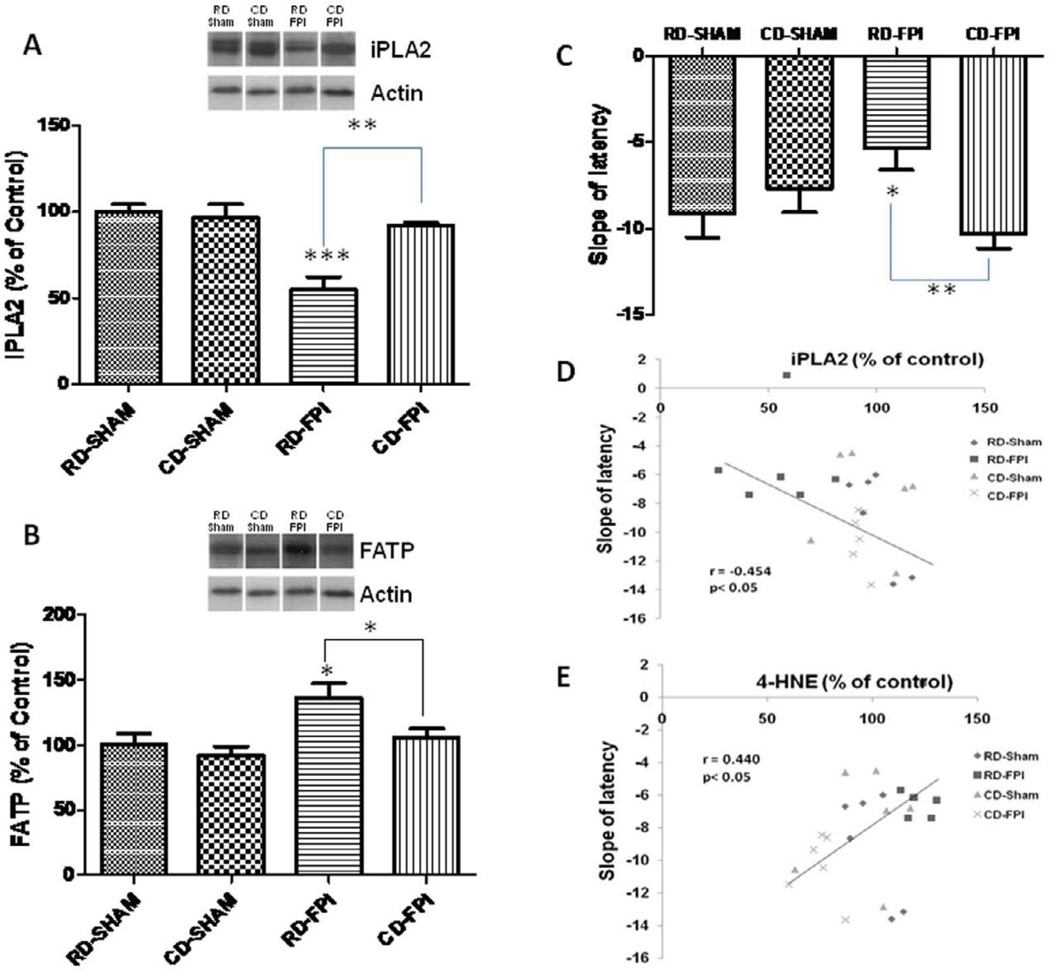
Figure 2.
(A–B) Effects of FPI and curcumin derivative treatment on molecular systems important for maintenance of plasma membrane homeostasis, and cognitive abilities. FPI decreased iPLA2 levels (A) while increased FATP levels (B) in the hippocampus. Representative Western blots for iPLA2 and FATP from all experimental groups in hippocampus are shown here. Dietary curcumin derivative supplementation significantly enhanced the levels of iPLA2 after FPI. (C) Slope of escape latency (the learning speed) to find the platform in training trial during Morris water maze test for each group of animals. FPI significantly decreased the learning speed in regular diet animals but the dietary curcumin derivative supplementation significantly improved the learning speed after FPI. (D) Correlation of slope of latency with the hippocampal levels of iPLA2. Slope of latency changed in inverse proportion to iPLA2 levels. The values were converted to percent of RD sham group (mean ± SEM). *p < 0.05, **p< 0.01, ***p< 0.001, ANOVA followed by post-hoc tests with Bonferroni’s comparisons. RD, regular diet; FPI, fluid percussion injury