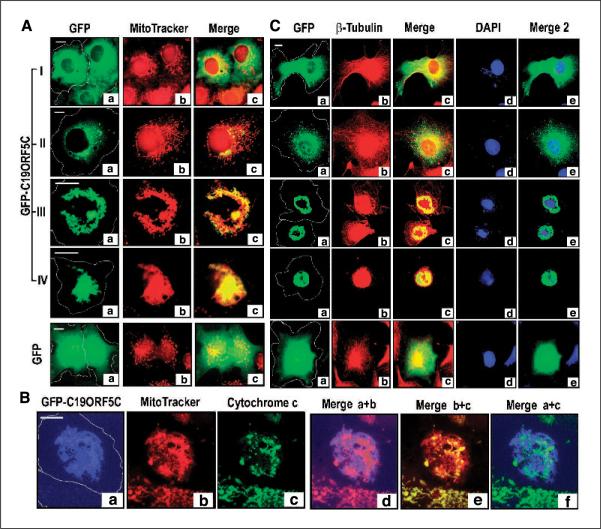
Figure 3.
MAGD caused by C19ORF5. A, relationship of GFP-C19ORF5C and mitochondria in type I to IV cells. Cell boundaries were determined and then outlined as described in Fig. 1. The green GFP signal (a) was merged with that of red MitoTracker (b) in Merge (c). Yellow, overlap of the GFP signal with mitochondria. B, relation of GFP-C19ORF5C-associated mitochondria with cytochrome c. To achieve maximum color contrast, the strong GFP signal from GFP-C19ORF5C was artificially assigned blue. The cytochrome c signal was assigned green. The overlap of blue GFP-C19ORF5C with red MitoTracker, red MitoTracker with green cytochrome c, or blue GFP-C19ORF5C with green cytochrome c is indicated by purple, yellow, or cyan in Merge d, e, or f, respectively. C, coincidence of microtubular collapse and DNA degradation with C19ORFC-associated mitochondrial aggregation. The green GFP signal from GFP-C19ORF5 (a) was analyzed with that of red β-tubulin immunochemical stain (b) in Merge (c) and blue DAPI DNA stain (d) in Merge 2 (e). Yellow in Merge is indicative of overlap of the GFP signal with tubulin and cyan in Merge 2 is indicative of overlap of the GFP signal with DAPI. Microtubules were visualized by immunoanalysis as described in Materials and Methods. Control cells transfected with GFP alone are indicated.