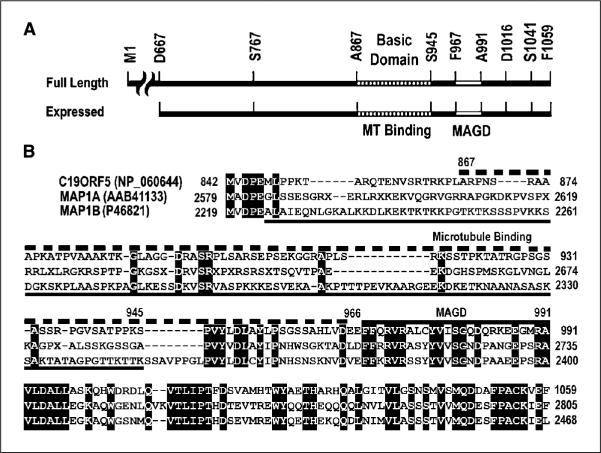
Figure 6.
Comparison of functional sequence domains in the COOH terminus of C19ORF5 to sequence of the light chains of MAP1A and MAP1B. A, sequence domain structure of C19ORF5. Full-length C19ORF5 and the 393–amino acid residue C19ORF5C (D667-F1059) with residues flanking constructs used in this study are indicated. A867-S945 indicates the highly basic microtubule-binding domain. F967-A991 is the MAGD domain. B, sequence alignment of human C19ORF5 with the light chains of MAP1A (MAP1A-LC2) and MAP1B (MAP1B-LC1). Identical residues in all three sequences are in black. Dashed bar (top), C19ORF5 sequence A867-E966 containing the microtubule-binding domain; bottom solid line, microtubule-binding domain of MAP1B (45); top solid bar, MAGD domain of C19ORF5.