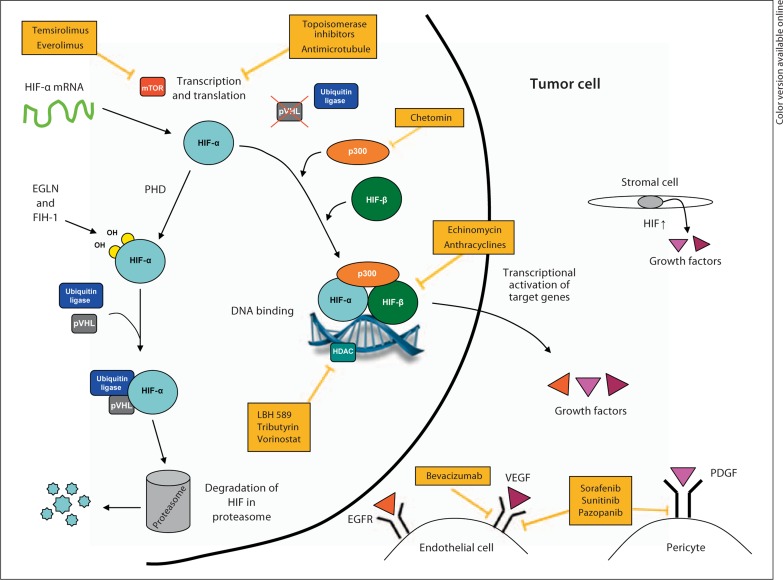
Fig. 1.
Diagram depicting the tumor microenvironment and mechanism of known HIF inhibitors. HIF-α is overexpressed in cancer cells and stromal cells, thus promoting tumor angiogenesis by inducing the production of VEGF and other proangiogenic factors. HIF inhibitors work by disrupting HIF-α protein synthesis, stability or transcriptional activity. PHD = Prolyl hydroxylase; pVHL = von Hippel-Lindau protein; HDAC = histone deacetylase; p300 = transcriptional coactivator p300; EGFR = epidermal growth factor receptor; EGLN = Egl-Nine gene; FIH-1 = factor inhibiting HIF-1.