Figure 8. Pharmacological properties of background K+ current.
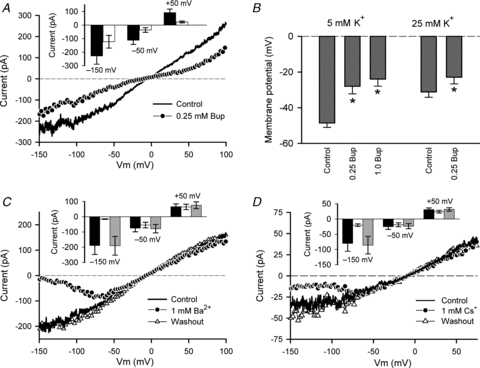
A, effect of 0.25 mm bupivacaine (Bup) on background K+ current I–V relation. A ramp voltage-clamp protocol was used to generate the I–V relation. External [K+] was 145 mm, pHo was 8.5. Inset shows plot of current magnitude (±SEM) at –150, –50 and +50 mV, in control (black) and with 0.25 mm Bup (white). Data pooled from 9 cells. B, effect of 0.25 and 1 mm Bup on RMP of HAC in 5 (n = 8) and 25 mm (n = 5) external K+. For 5 mm K+, * indicates significant differences (P < 0.001) compared with control (C); there was no significant difference between 0.25 and 1.0 mm Bup (repeated measures ANOVA). For 0.25 mm Bup in 25 mm K+, P = 0.0127, paired t test. C, effect of 1 mm Ba2+ on background K+ current (ramp protocol) I–V relation. External [K+] was 145 mm, pHo was 8.5. Ba2+ blocked the K+ current in a voltage-dependent, reversible manner. Inset shows current magnitude at three membrane potentials of the I–V relation, –150, –50 and +50 mV, in control (black), with 1 mm Ba2+ (white), and after washout of Ba2+ (grey). Data pooled from 4 cells. D, effect of 1 mm Cs+ on background K+ current (ramp protocol) I–V relation. External [K+] was 145 mm, and pHo was 7.4. Inset shows current magnitude at three membrane potentials of the I–V relation, –150, –50 and +50 mV, in control (black), with 1 mm Cs+ (white), and after washout of Cs+ (grey). Data pooled from 5 cells.
