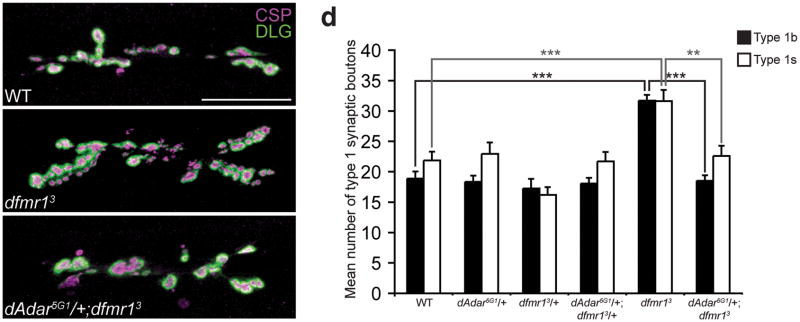
Figure 6. Reduction of dAdar dosage rescues the dfmr13 null NMJ defects in L3 larvae.
(a–c) Confocal images of WT (a), dfmr13 (b), and dAdar5G1/+;dfmr13 (c) L3 larval NMJs. Larvae were stained for CSP (presynaptic, magenta) and DLG (postsynaptic, green). Type 1b and type 1s synaptic boutons were distinguished as described in Fig. 2. No noticeable differences in CSP and DLG intensity were observed across genotypes. Scale bar represents 50 μm. (d) The reduction of dAdar dosage rescues the dfmr1 synaptic bouton phenotype, as revealed by quantification of average number of type 1b (black bars) and type 1s (white bars) synaptic boutons for trans-heterozygous genotypes using the dAdar5G1 and dfmr13 mutant alleles. All images and quantification were performed using muscles 6/7, hemisegment A3. n≥16 for each genotype. Error bars denote s.e.m. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, analyzed by one-way ANOVA, p<0.0001 overall, Tukey-Kramer post-test.