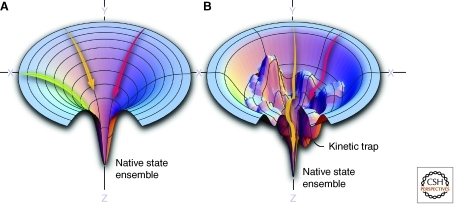
Figure 1.
Energy landscape perspective on protein folding. In this view, individual positions in the X-Y-planes correspond to different protein conformations, which diminish in number as the polypeptide chain forms increasing numbers of native intrachain hydrophobic and electrostatic contacts, lowering the internal free energy as the protein approaches its native state conformational ensemble along the Z-axis. (A) A smooth folding funnel reveals the numerous pathways that a polypeptide chain can take to reach the folded conformational ensemble, reflected by the arrows moving down the folding free energy diagram. (B) A rougher folding free energy landscape also indicates that multiple parallel paths can be followed to reach the native state ensemble, however occasionally the polypeptide chain can get kinetically trapped in a folding intermediate (indicated by the red arrow).