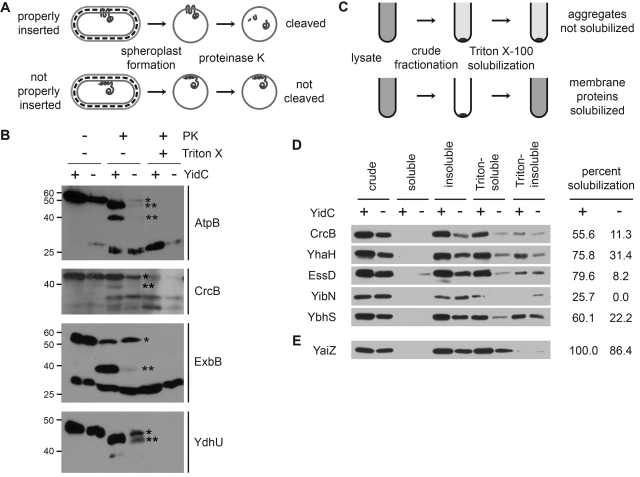
FIG 2 .
Membrane proteins mislocalized in the absence of YidC are YidC dependent for membrane insertion. (A and B) Proteinase K accessibility assay of spheroplasts depleted of YidC or not depleted of YidC (see Materials and Methods). (A) Experimental approach. (B) Screen hits that displayed reduced protease accessibility following YidC depletion. The spheroplasts were treated with proteinase K (PK) (+) in the protease accessibility assay. Cells pretreated with Triton X-100 (+) to promote lysis served as a control for proteolysis. In the absence of YidC (−), increased abundance of full-length protein (*) and decreased abundance of major cleavage product(s) (**) was observed. The positions of molecular mass standards (in kilodaltons) are shown to the left of the gels. (C to E) Differential fractionation of screen hits into Triton X-100-soluble and -insoluble membrane fractions following synthesis in cells depleted of YidC or not depleted of YidC. (C) Experimental approach. (D) Screen hits that displayed reduced Triton X-100 solubility when synthesized in the absence of YidC. (E) A screen nonhit that displayed comparable Triton X-100 solubilities when synthesized in the presence and absence of YidC. Western blots using antibody to GFP are shown. The cell fractions are as follows: crude, whole-cell proteins; soluble, soluble cytoplasmic and periplasmic proteins; insoluble, membranes and other insoluble proteins; Triton-soluble, Triton X-100-soluble fraction of insoluble proteins; Triton-insoluble, Triton X-100-insoluble fraction of insoluble proteins. The loads were proportional and normalized to the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) of culture. Percent solubilization, the ratio of Triton-soluble band to crude fraction band as determined by band densitometry. Images are representative.