FIG 3 .
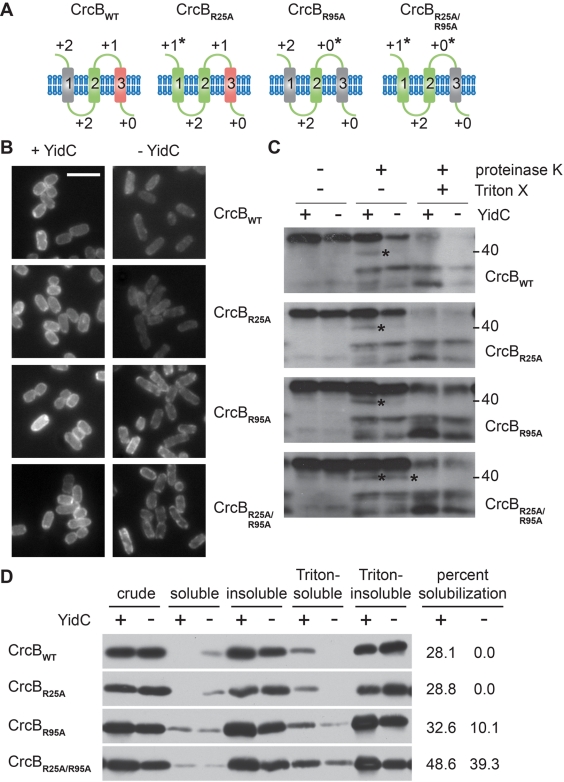
The distribution of positively charged residues determines the dependence of CrcB on YidC for membrane insertion. (A) Topological illustrations of the cytoplasmic membrane protein CrcB (22) and variants with altered charge balances. Balanced transmembrane segments (green), charge-neutral transmembrane segments (grey), and charge-unbalanced transmembrane segments (red) are shown. Charge balance altered by mutagenesis is indicated by an asterisk. (B) Subcellular localization of GFP-tagged CrcB (CrcB-GFP) variants in the presence or absence of YidC. Bar, 5 µm. (C and D) Protease susceptibility (C) or differential fractionation into Triton X-100-soluble and -insoluble membrane fractions (D) of CrcB-GFP variants following synthesis in the presence or absence of YidC (see Fig. 2 legend and Materials and Methods). The position of a proteolytic product detected only in the absence of YidC for CrcBWT but in increasing amounts in the absence of YidC for the balanced variants is indicated by an asterisk. Images are representative; all images in each panel are from the same Western blot or same microscopy experiment.