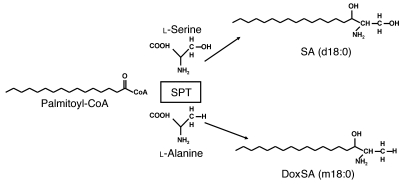
Figure 1. Sphingolipid de novo synthesis is initiated by the condensation of an activated fatty acid (normally palmitoyl-CoA) and l-serine to form SA.
This reaction is catalyzed by SPT. In HSAN1, the SPT shows a shift in substrate specificity to alanine, which results in the formation of an atypical class of dSLs. For SA and doxSA (1-deoxysphinganine), the number of hydroxyl groups is indicated by m (mono-) and d (di-), followed by the number of carbons; the second number indicates the double bonds.