Fig. 4.
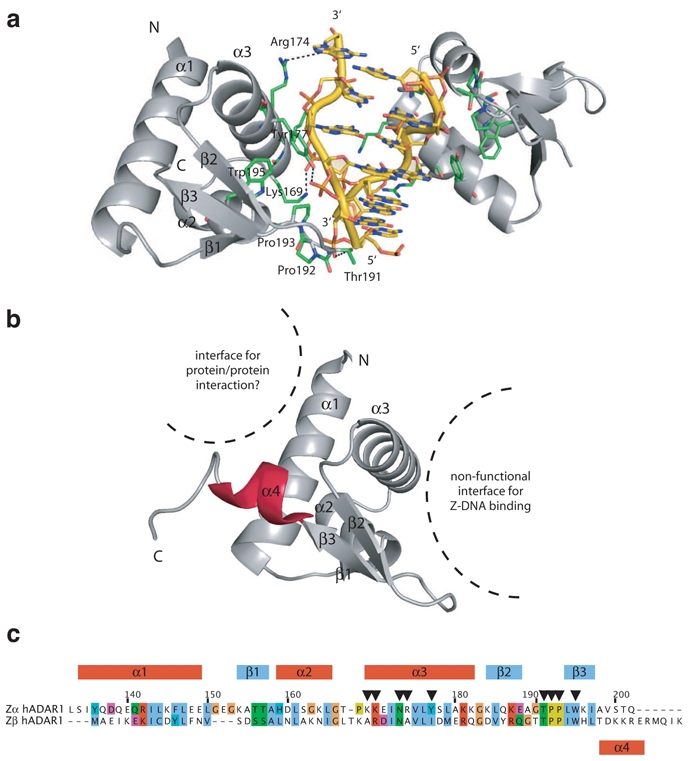
Structures of ADAR Z-DNA binding domains. a) Structure of the Zα domain of ADAR1 in complex with Z-DNA (CG)3 showing contacts with the phosphate backbone via helix α1 and beta hairpin β2-β3. b) Structure of the Zβ domain of ADAR1 in its free state with a nonfunctional Z-DNA binding surface and a potential protein/protein interaction surface. The additional helix α4 is shown in red. c) Sequence alignment of hADAR1 Zα and Zβ domains. The alignment is colored by amino acid conservation and properties. Common secondary structure elements are shown on top of the alignment. The position of the additional helix α4 is shown below. Residues of Zα involved in direct or water-mediated contacts with Z-DNA are reported with black arrows. Some of these residues are not conserved in Zβ. Residue numbers correspond to the one of Zα.
