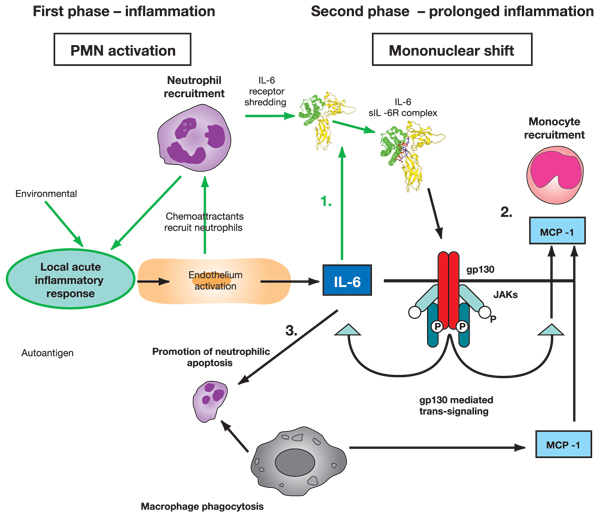
Figure 2.
Possible role played by IL-6 in the shift from acute to chronic inflammation. Stage 1: following acute inflammatory response, IL-6 can bind with sIL-6R. Stage 2: trans-signalling through gp130 leads to monocyte recruitment. Stage 3: prolonged IL-6 leads to neutrophilic apoptosis, phagocytosis and mononuclear accumulation at the site of injury. IL, interleukin; JAK, Janus activated kinase; MCP, monocyte chemoattractant protein; PMN, polymorphonuclear neutrophil; sIL-6R, soluble IL-6 receptor.