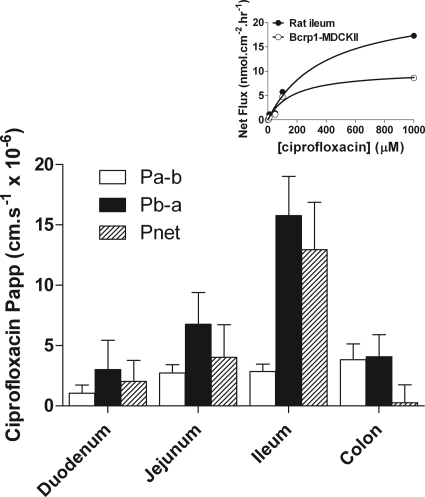
Fig. 4.
Ciprofloxacin permeability across excised sections of rat duodenum, jejunum, ileum, and colon. Ciprofloxacin permeability was determined in the apical-to-basal (Pa-b) and basal-to-apical (Pb-a) directions in adjacent tissue segments giving net permeability (Pnet = Pb-a − Pa-b). Total ciprofloxacin concentration in the donor compartment was 30 μM. Ciprofloxacin concentrations were determined by HPLC-tandem mass spectrometry. Data are mean ± S.E.M. of n = 3 separate animals. Inset, dose-response curves showing the net flux (Jnet) of increasing concentrations of ciprofloxacin in excised rat ileum (●) and bcrp1-MDCKII monolayers (○).