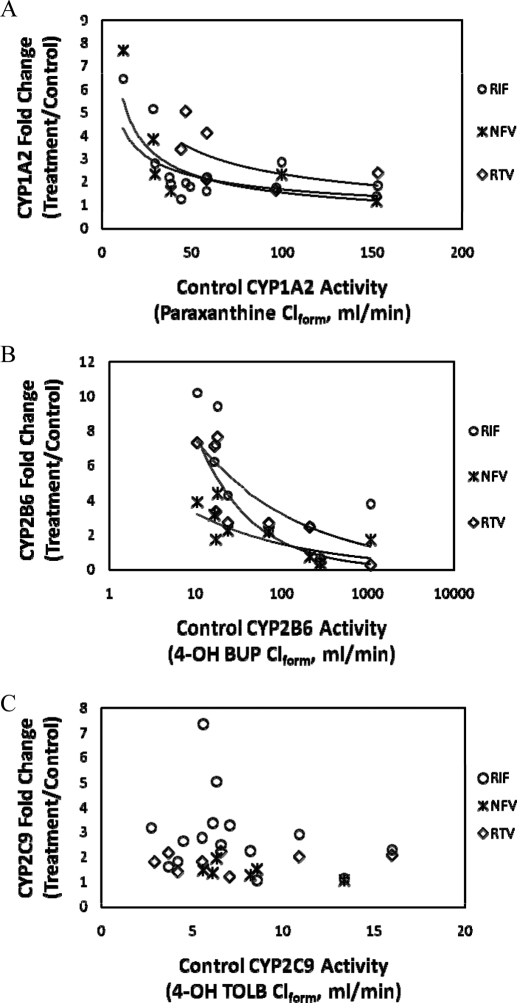
Fig. 4.
Correlation analysis of observed in vivo induction of CYP1A2 (A), CYP2B6 (B), and CYP2C9 (C) after treatment with RIF, NFV, or RTV relative to control P450 activity (4-OH BUP, paraxanthine, or 4-OH TOLB Clform, respectively). In vivo CYP2B6 (A) and CYP1A2 (B) but not CYP2C9 (C) fold induction by RTV, NFV, or RIF treatment was inversely and nonlinearly correlated with basal activity. Those subjects with the highest basal CYP2B6 or CYP1A2 activity tended to show only modest induction of in vivo activity of these enzymes after treatment with the inducers. Note the log scale for control CYP2B6 activity, whereas CYP1A2 and CYP2C9 are displayed on a linear scale. Regression analysis results for CYP1A2 (RIF, y = 12.7x−0.44 R2 = 0.44; NFV, y = 24.1x−0.6 R2 = 0.70; and RTV, y = 29.9x−0.55 R2 = 0.39) and CYP2B6 (RIF, y = 17.4x−0.37 R2 = 0.47; NFV, y = 7.1x−0.34 R2 = 0.45; and RTV, y = 37.3x−0.68 R2 = 0.83).