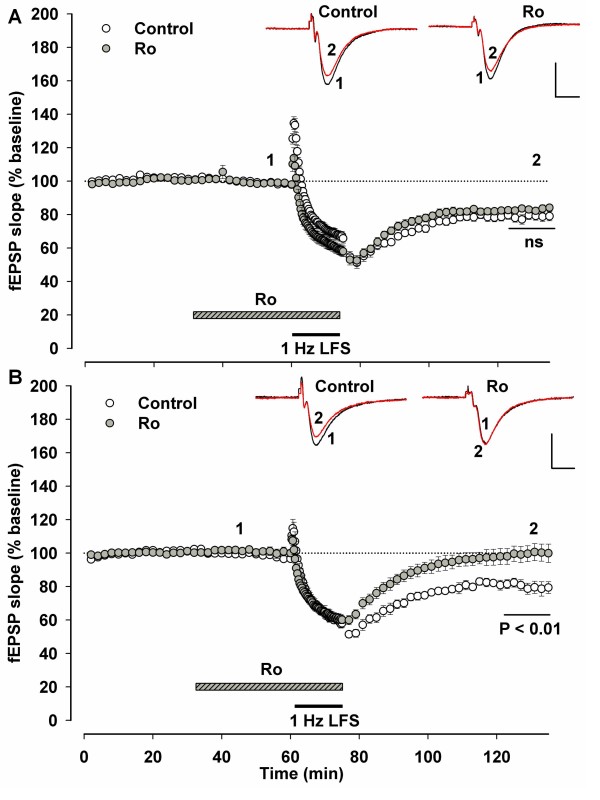
Figure 1.
LTD in sagittal and coronal slices has different GluN2B-dependence. Hippocampal slices (400 μM) prepared in either sagittal (A) or coronal (B) orientations, both with CA3 attached, were used for extracellular recordings of field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs) in area CA1. After a stable baseline recording period (at least 30 minutes) the GluN2B-selective antagonist Ro 25-6981 (5 μM, Ro) was applied and stimulation at 0.03 Hz continued for another 30 minutes until a 1 Hz, 15 minute low frequency stimulation (LFS) at baseline intensity, also in the presence of Ro. Drug application was stopped at the end of LFS and the magnitude of LTD was quantified in the last ten minutes of the hour after LFS. In the slices of either orientation that were not treated with Ro, LFS induced LTD. Likewise, in the sagittal slices, Ro did not prevent the induction of LTD (A) although D-AP5 (50 μM) did (data not shown). However, in the coronal slices treated with Ro, LFS did not induce LTD (B). Scale bars represent 10 ms and 0.5 mV.