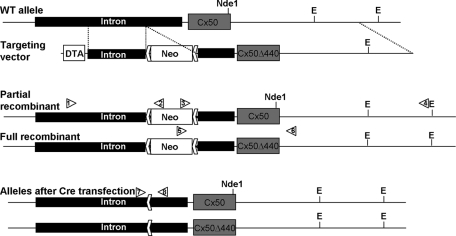
FIGURE 5:
Construction of the Cx50Δ440 knock-in mouse. The Cx50 coding sequence is contained in a single exon following a 5.5-kb intron. The targeting vector added a floxed PGK–neomycin resistance cassette inside the intron and a PGK–diphtheria toxin A chain cassette outside the 5′ homology and contained a three-base deletion in the coding sequence deleting the ultimate C-terminal residue. Initial screening for homologous recombinants used PCR amplification with primers outside the 5′ homology arm (1) and in the neo cassette (2). A secondary screen verified 3′ structure using primers in the neo cassette (3) and outside the 3′ homology arm (4). Because the Cx50Δ440 mutation eliminated an Nde1 site, the presence of the mutation was confirmed by restriction digestion. In addition to fully recombined clones, several were identified with partial recombination, resulting in homologous integration of the neo cassette but leaving the native coding sequence, providing an ideal negative control. Recombinant ES clones were then transfected with cre recombinase and screened for neo excision using primers P7 and P8.