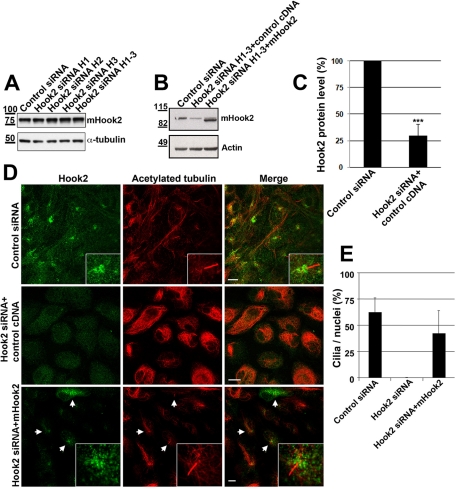
FIGURE 3:
Exogenous mouse Hook2 rescues defect in ciliogenesis by Hook2 depletion in human ARPE19 cells. (A) 4T1 mouse cells were transiently transfected with control or different human Hook2 siRNA as indicated. After 7 d of incubation, the cells were lysed and tested by WB for Hook2 and α-tubulin production. Molecular weights are indicated on the left in kilodaltons. Note that human Hook2 siRNAs do not deplete mouse Hook2. (B–E) ARPE19 Hook2 siRNA transiently transfected cells were further transfected with an empty vector or mouse Hook2 cDNA and compared with control cells. After 7 d, cells were either processed for WB analysis of Hook2 and actin (B, and quantification of human Hook2 depletion in C) or fixed in PFA and compared by immunofluorescence and confocal microscopy analysis for their ability to promote ciliogenesis (D). Bar, 10 μm; inset magnification, ×15. Arrows indicate cells that express mouse Hook2 cDNA. (E) Quantification of ciliogenesis rescue. Bars represent the percentage of identified cilia per nuclei in each condition. Error bars, SD.