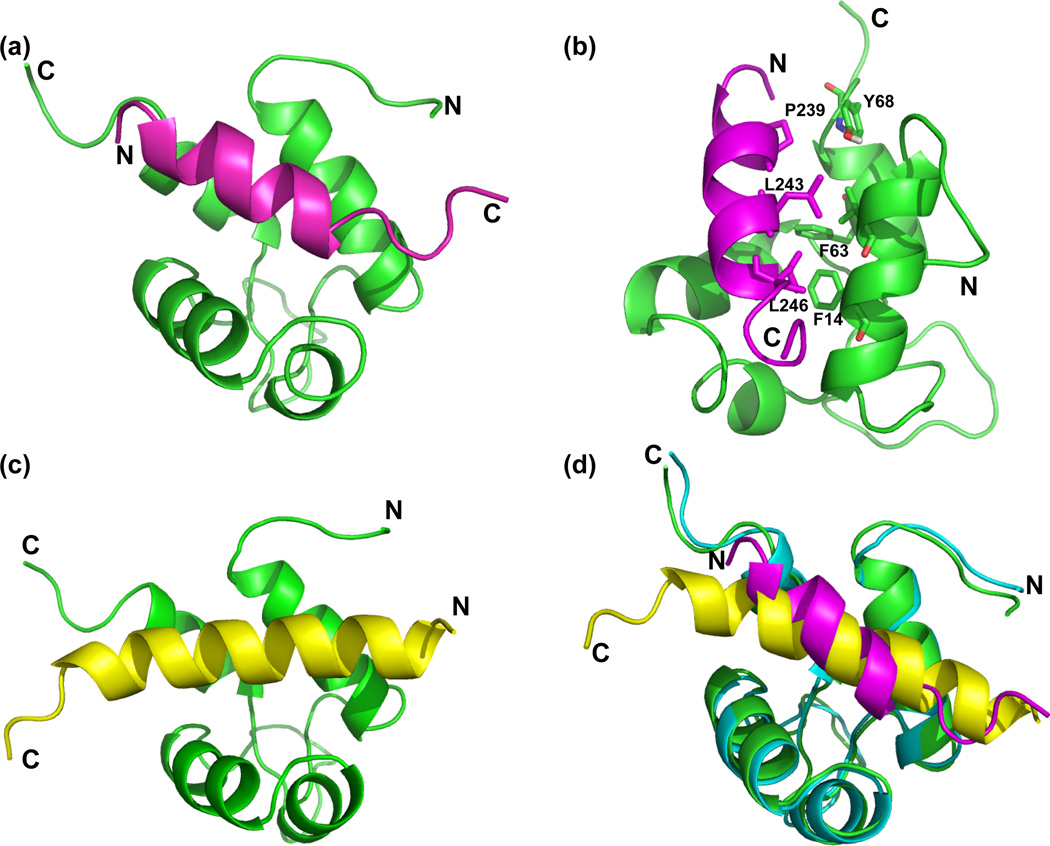
Figure 6.
Comparison of the Act-EF34 complex with palladin and titin peptides. (a) Ribbon diagram showing a representative palladin complex structural model. Act-EF34 is shown in green and palladin in magenta, with termini labeled to highlight orientation. (b) Critical residues used in docking are highlighted. The backbone atoms associated with the hydrophobic Act-EF34 Phe 14, Phe 63, and Tyr 68 residues that were utilized as restraints in docking. Palladin residues, Leu 243 and 246, are hydrophobic residues in the first and fourth position of the ‘1-4-5-8’ motif. These residues were mutated, found to abolish binding to Act-EF34, and then used as restraints for docking. (c) For comparison, the ribbon diagram of the complex between Act-EF34 (green) and titin’s seventh Z-repeat in yellow is shown (Act-EF34—Zr7; PDB ID: 1H8B). (d) Structural alignment of palladin-bound (green with magenta peptide) and titin-bound (cyan with yellow) Act-EF34.