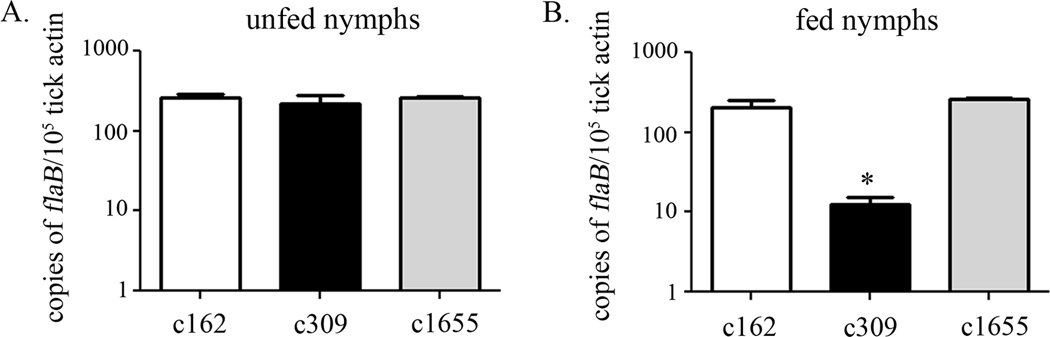
Figure 9.
Bb CoADR promotes survival of spirochetes within fed, but not flat, nymphs. Ixodes scapularis nymphs were rectally-infused with equivalent densities of wild-type (c162), cdr mutant (c309), and complemented (c1655) clones of B. burgdorferi. (A) After a ten day ‘rest’ period, relative B. burgdorferi burdens in unfed ticks were analyzed by qRT-PCR; the number of copies of the B. burgdorferi flaB transcript were normalized to tick β-actin RNA. The remainder of the rectally-infused nymphs were then allowed to feed upon SCID mice to repletion. (B) B. burgdorferi burdens in fed nymphs were monitored by qRT-PCR. The asterisk (*) denotes a significant difference between spirochetes in the midguts of fed nymphs infused with the cdr mutant compared to those infused with either the wild-type or the complement (P < 0.05). The data represent the average of four replicates of qRT-PCR analysis on two pools of three ticks (unfed) or 1–2 ticks (fed) from a representative experiment.