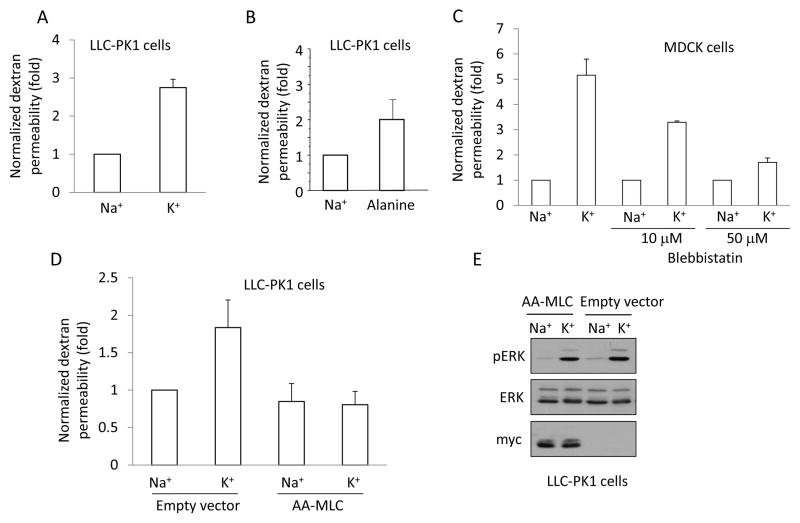
Figure 7. Depolarization elevates paracellular permeability in a pMLC-dependent manner.
A–D. LLC-PK1 (A, B) or MDCK (C) or AA-MLC expressing LLC-PK1 cells (D) were grown to confluence on Costar Transwell filters. The medium in both the top and bottom compartments was replaced by Na+- or K+-medium and the cells were exposed to 2 mg/ml FITC-labelled dextran (4 kDa) added apically. FITC fluorescence was measured in samples taken from the bottom compartment after 3 hours. The fluorescence values obtained in the triplicate measurements of each experiment were averaged and normalized to the control. The following treatments were used as indicated: Na+ or K+ -medium (A,C, D); 20 mM alanine in Na+-medium (B); 10 or 50 μM blebbistatin pretreatment in Na+ medium for 30 minutes followed by Na+- or K+-medium supplemented with blebbistatin (C). The graphs show the mean ± S.E. from n≥3 experiments. E. Depolarization induced similar ERK phosphorylation in AA-MLC and control cells. Empty vector- or AA-MLC-transfected LLC-PK1 cells were treated with Na+- or K+-medium for 5 minutes. The cells were lysed and pERK, ERK and myc-tagged AA-MLC were detected by Western blotting.