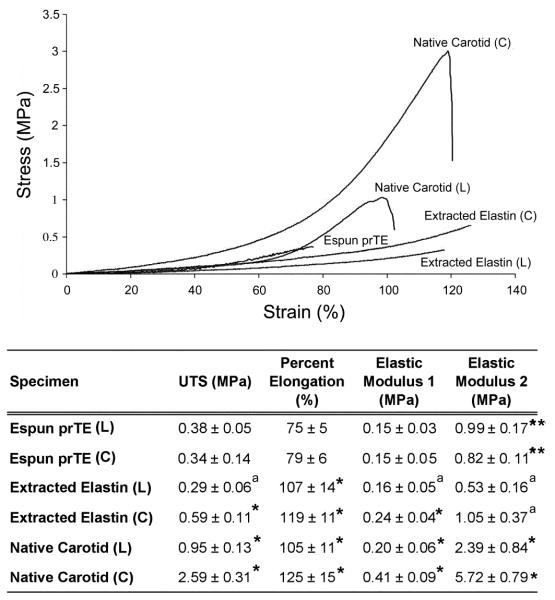
Figure 6.
Mechanical properties of the electrospun prTE scaffolds. (Top) Representative stress-strain curves of electrospun prTE, extracted porcine elastin, and native porcine carotid arteries. (Bottom) Table of mechanical properties including ultimate tensile strength (UTS), percent elongation at failure, and elastic moduli of electrospun prTE compared to extracted porcine elastin and native porcine carotid arteries. The UTS and elastic moduli of electrospun prTE were not significantly different from the extracted elastin in the longitudinal direction. Note: aindicates no significant difference (ANOVA, Tukey post hoc, p > 0.05), compared to electrospun prTE in the same orientation, *indicates a significant difference (ANOVA, Tukey post hoc, p < 0.05) for comparisons to electrospun prTE in the same orientation, and **indicates p < 0.01, t-test.