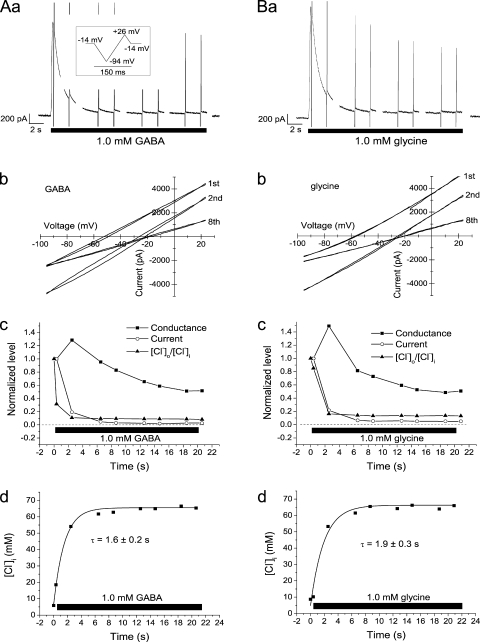
Figure 5.
Rapid changes in [Cl−]i during GABA and glycine application. (A and B) Currents, conductances, and [Cl−]i during application of either 1.0 mM GABA (A) or 1.0 mM glycine (B) to the same neuron. Raw currents shown in A (a) and B (a). (Gaps are a result of limitations of the sampling protocol used.) Vm = −14 mV, except during the voltage ramps. Inset shows voltage protocol during each ramp sequence. (A, b, and B, b) I-V relation for the currents recorded during the first, second, and eighth ramp sequences, as indicated. Note the large shift in Vrev and the slight increase in slope from the first to the second ramp sequence. (A, c, and B, c) Comparison of the time course for current, conductance, and the ratio [Cl−]o/[Cl−]i. (The ratio was used to plot a decaying function of time to simplify comparison.) [Cl−]o/[Cl−]i normalized to that before agonist application, current, and conductance to the values at the first ramp sequence, close to peak current. (A, d, and B, d) Time course of [Cl−]i, computed as described in Results. Smooth curves are fitted exponentials with time constants of 1.6 s (A, d) and 1.9 s (B, d). Currents were recorded in gramicidin-perforated patch mode (A and B).