Figure 6.
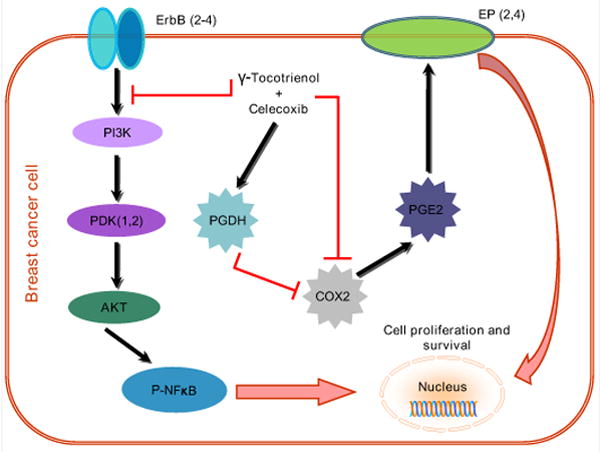
Schematic illustration of the COX-2 dependent and independent mechanisms involved in mediating the synergistic antiproliferative effects of combined γ-tocotrienol and celecoxib treatment. The COX-2-dependent mechanism involve a suppression in COX-2 and PGE2 levels and a corresponding increase in PGDH levels, while the COX-2-independent mechanisms involve a reduction in the levels and EGF-dependent activation ErbB2-4 receptor levels and subsequent reductions in downstream Akt and NFκB mitogenic signaling.
