Abstract
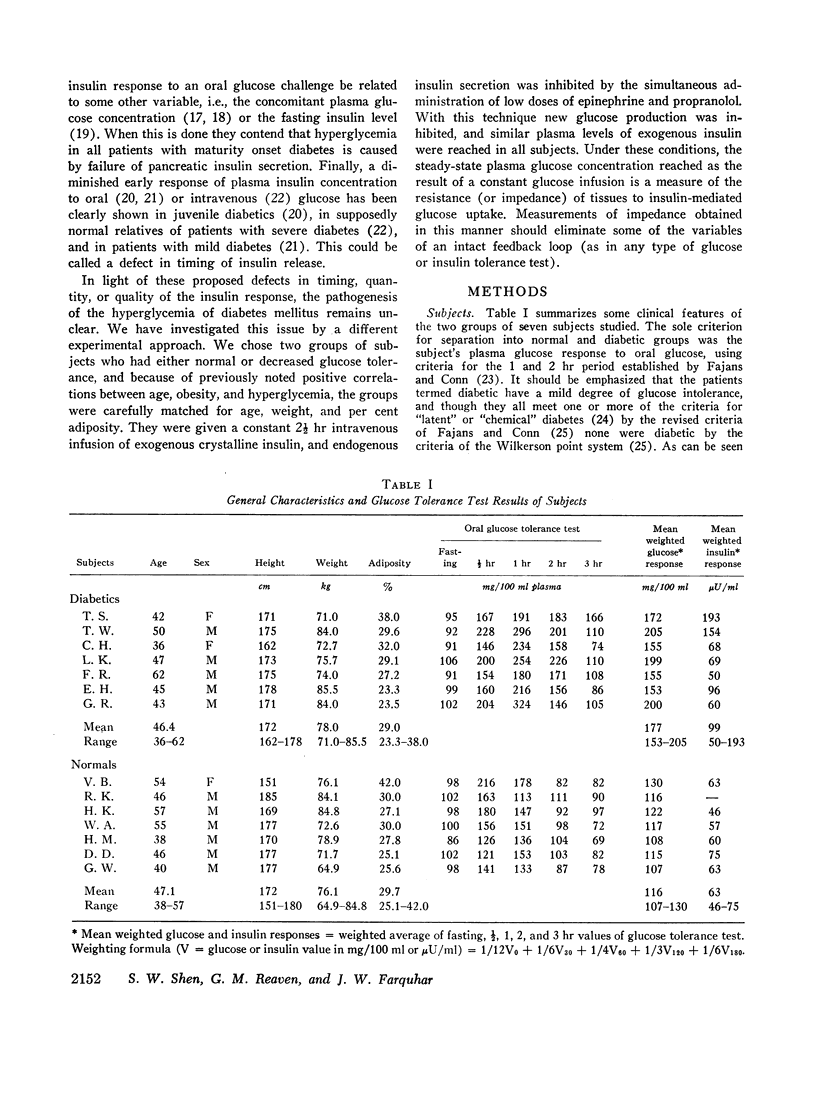
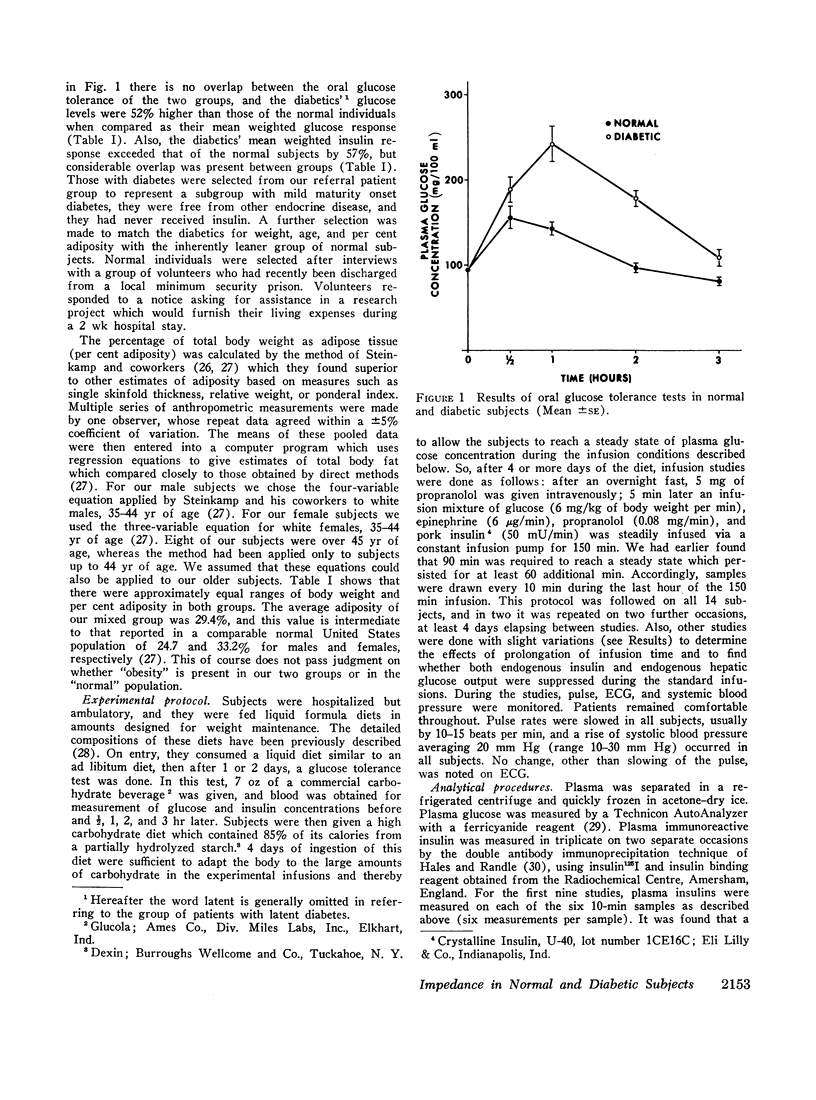
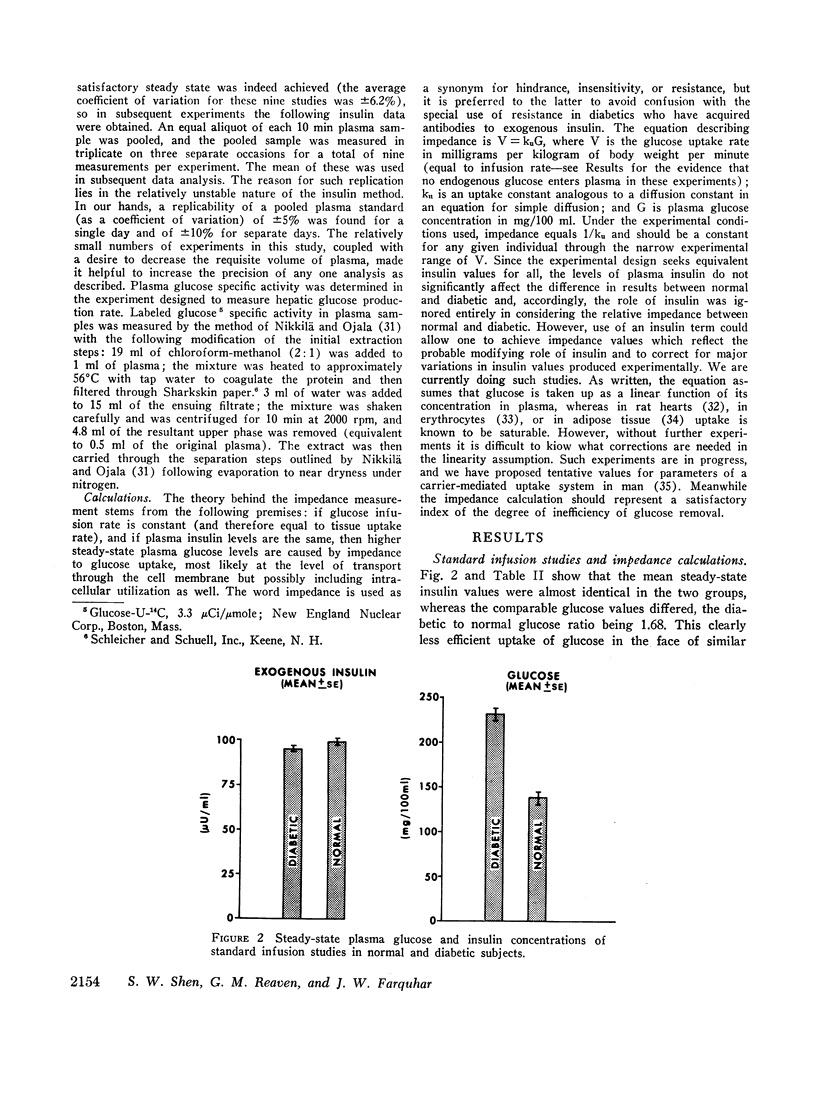
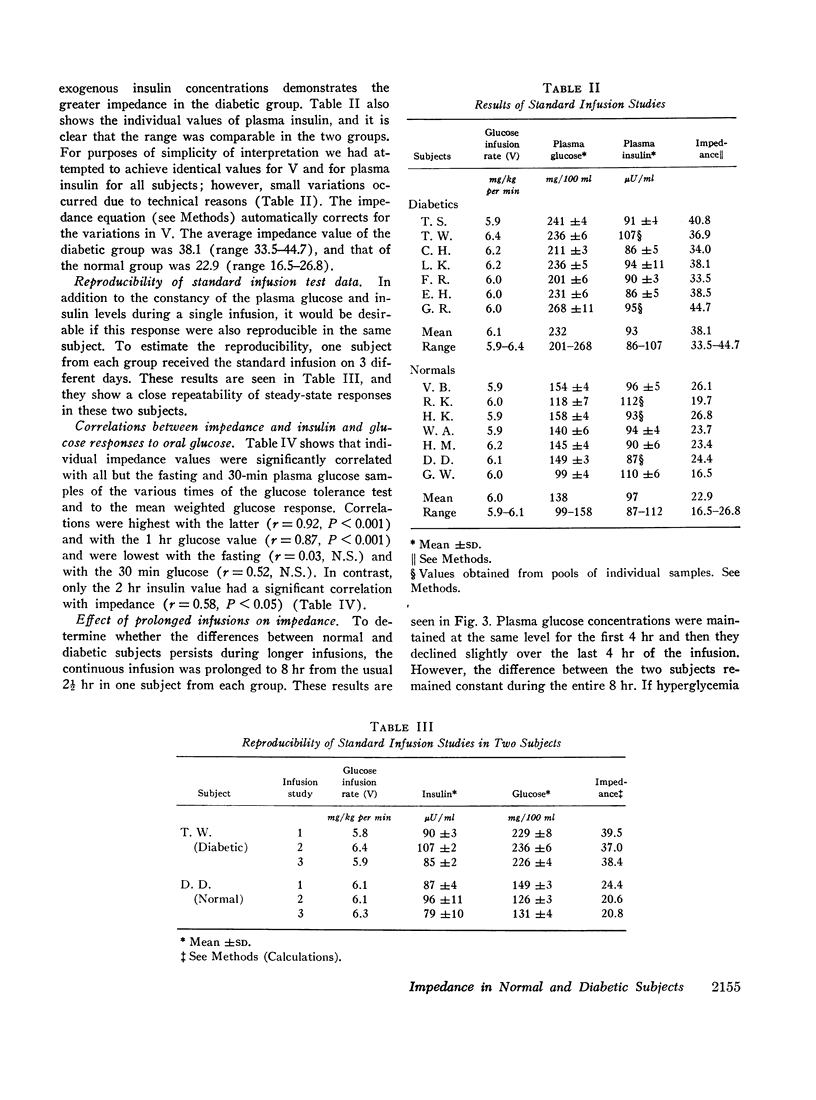
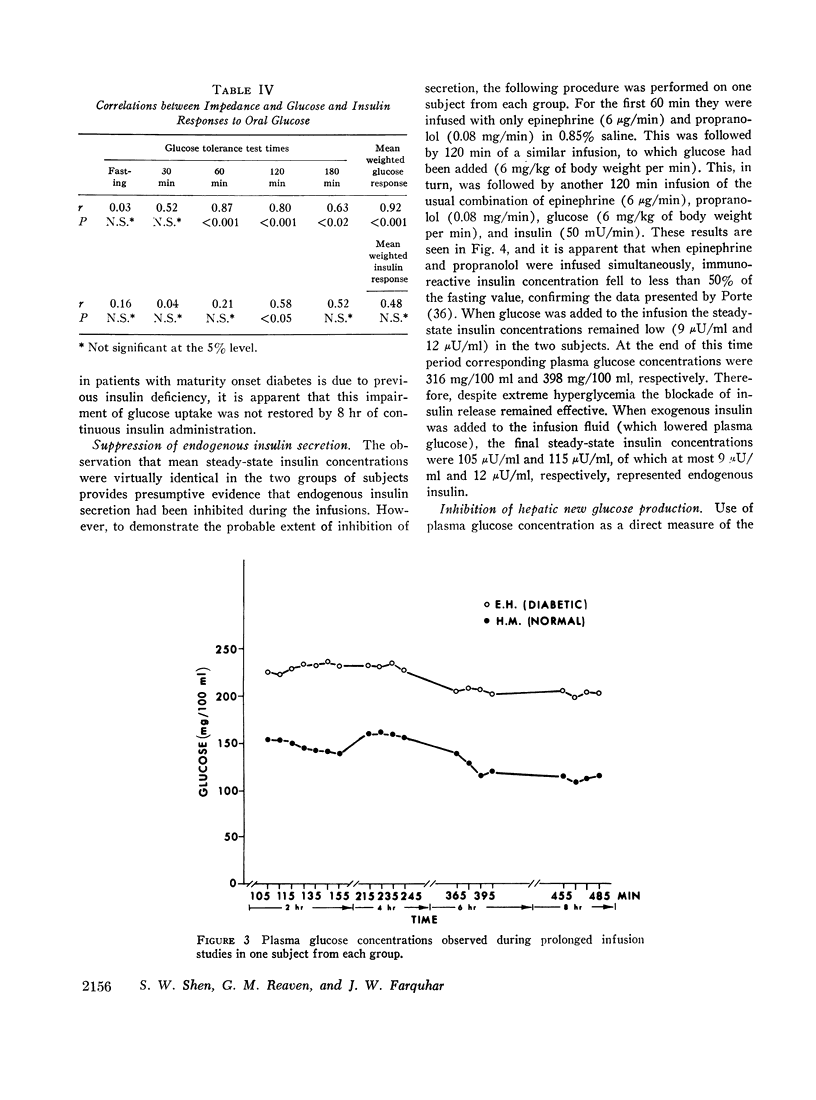
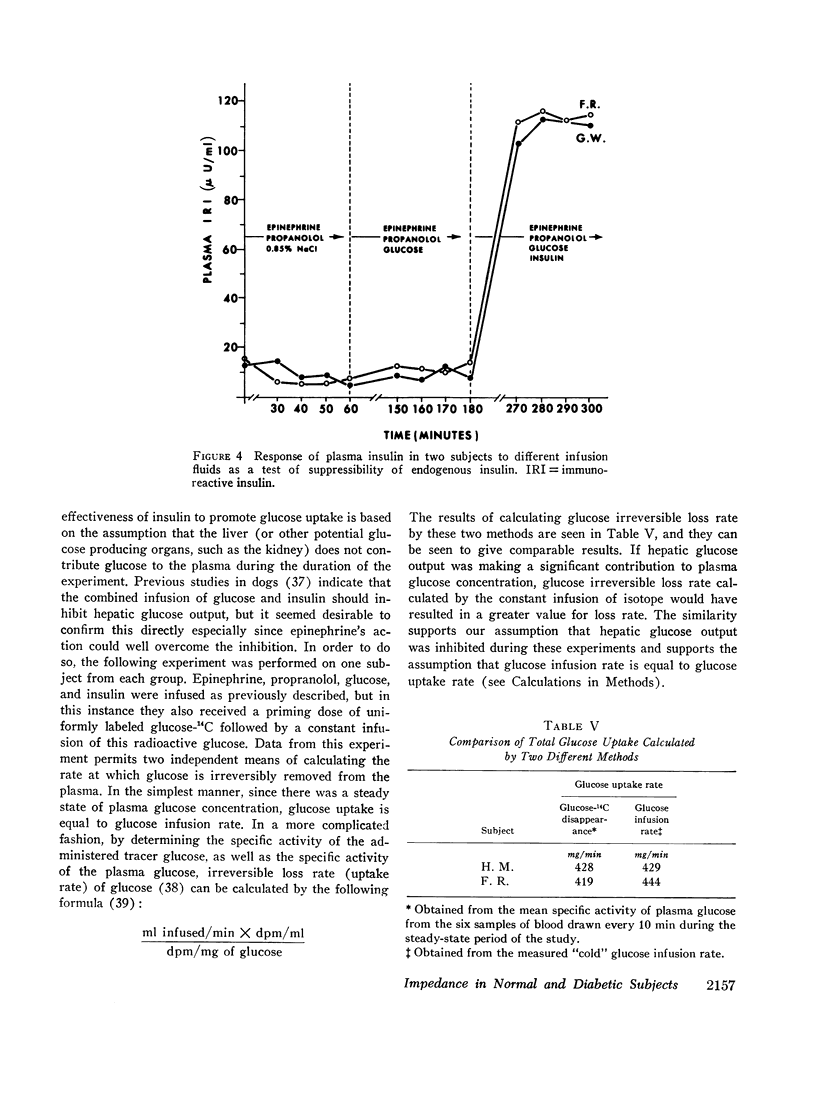
A technique was devised for a more accurate measurement than has been heretofore possible of one of the factors responsible for hyperglycemia in the complex syndrome of diabetes. This factor is termed impedance and represents the tissues' insensitivity or resistance to insulin-mediated glucose uptake. It was measured by use of steady-state exogenous insulin and glucose infusions during a period of pharmacological suppression of endogenous insulin secretion. Endogenous new glucose production was also inhibited. Impedance as calculated is a direct function of steady-state glucose concentrations, since exogenous insulin concentrations were similar in all studies. Two groups of normal weight subjects were studied. One had maturity onset latent diabetes, and the other (matched for age, weight, and per cent adiposity) was normal. Impedance was closely reproducible in the same individual and remained relatively constant during prolonged infusions. The diabetics had average infusion glucose concentrations (and thus impedance) 68% higher than the normal group, and it is of note that their previously measured glucose intolerance differed by a similar degree; that is, the diabetic's intolerance (as defined by mean weighted plasma glucose response after oral glucose) was 52% greater than that of the normal individuals.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAKER N., SHIPLEY R. A., CLARK R. E., INCEFY G. E. C14 studies in carbohydrate metabolism: glucose pool size and rate of turnover in the normal rat. Am J Physiol. 1959 Feb;196(2):245–252. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagdade J. D., Bierman E. L., Porte D., Jr The significance of basal insulin levels in the evaluation of the insulin response to glucose in diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1967 Oct;46(10):1549–1557. doi: 10.1172/JCI105646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson S. A., Yalow R. S. Insulin in blood and insulin antibodies. Am J Med. 1966 May;40(5):676–690. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COMBES B., ADAMS R. H., STRICKLAND W., MADISON L. L. The physiological significance of the secretion of endogenous insulin into the portal circulation. IV. Hepatic uptake of glucose during glucose infusion in non-diabetic dogs. J Clin Invest. 1961 Sep;40:1706–1718. doi: 10.1172/JCI104393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROFFORD O. B., RENOLD A. E. GLUCOSE UPTAKE BY INCUBATED RAT EPIDIDYMAL ADIPOSE TISSUE. CHARACTERISTICS OF THE GLUCOSE TRANSPORT SYSTEM AND ACTION OF INSULIN. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3237–3244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerasi E., Luft R. "What is inherited--what is added" hypothesis for the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1967 Sep;16(9):615–627. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.9.615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson P. C., Albrink M. J. Insulin resistance in hyperglyceridemia. Metabolism. 1965 Oct;14(10):1059–1070. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(65)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAJANS S. S., CONN J. W. The early recognition of diabetes mellitus. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1959 Sep 25;82:208–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1959.tb44901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar J. W., Frank A., Gross R. C., Reaven G. M. Glucose, insulin, and triglyceride responses to high and low carbohydrate diets in man. J Clin Invest. 1966 Oct;45(10):1648–1656. doi: 10.1172/JCI105472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman L. A., Doeblin T. D., Emerling F. G. Diabetes in the Seneca Indians. Plasma insulin responses to oral carbohydrate. Diabetes. 1969 Jan;18(1):38–43. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genuth S. M., Bennett P. H., Miller M., Burch T. A. Hyperinsulinism in obese diabetic Pima Indians. Metabolism. 1967 Nov;16(11):1010–1015. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(67)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graber A. L., Wood F. C., Jr, Williams R. H. Serum immunoreactive insulin response during prolonged glucose infusions in nondiabetic and diabetic humans. Diabetes. 1967 Mar;16(3):145–149. doi: 10.2337/diab.16.3.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALES C. N., RANDLE P. J. Immunoassay of insulin with insulin-antibody precipitate. Biochem J. 1963 Jul;88:137–146. doi: 10.1042/bj0880137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreisberg R. A., Boshell B. R., DiPlacido J., Roddam R. F. Insulin secretion in obesity. N Engl J Med. 1967 Feb 9;276(6):314–319. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196702092760603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEFEVRE P. G., MCGINNISS G. F. Tracer exchange vs. net uptake of glucose through human red cell surface. New evidence for carrier-mediated diffusion. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Sep;44:87–103. doi: 10.1085/jgp.44.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN H. E., HENDERSON M. J., REGEN D. M., PARK C. R. Regulation of glucose uptake in muscle. I. The effects of insulin and anoxia on glucose transport and phosphorylation in the isolated, perfused heart of normal rats. J Biol Chem. 1961 Feb;236:253–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin F. I., Pearson M. J., Stocks A. E. Glucose tolerance and insulin insensitivity. Lancet. 1968 Jun 15;1(7555):1285–1286. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NIKKILAE E. A., OJALA K. GLUCONEOGENESIS FROM GLYCEROL IN FASTING RATS. Life Sci. 1964 Mar;3:243–249. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(64)90066-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. L., Pildes R. S., Chao K. L., Cornblath M., Kipnis D. M. Juvenile diabetes mellitus, a deficiency in insulin. Diabetes. 1968 Jan;17(1):27–32. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen E. P., Richenderfer L., Ginsberg-Fellner F. Plasma glucose, free fatty acids, and immunoreactive insulin in sixty-six obese children. Studies in reference to a family history of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1968 May;17(5):261–269. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.5.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perley M., Kipnis D. M. Plasma insulin responses to glucose and tolbutamide of normal weight and obese diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1966 Dec;15(12):867–874. doi: 10.2337/diab.15.12.867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porte D., Jr A receptor mechanism for the inhibition of insulin release by epinephrine in man. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):86–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI105514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Farquhar J. W. Steady state plasma insulin response to continuous glucose infusion in normal and diabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1969 May;18(5):273–279. doi: 10.2337/diab.18.5.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M., Lerner R. L., Stern M. P., Farquhar J. W. Role of insulin in endogenous hypertriglyceridemia. J Clin Invest. 1967 Nov;46(11):1756–1767. doi: 10.1172/JCI105666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimoin D. L., Saiki J. H. Diabetes mellitus among the Navajo. II. Plasma glucose and insulin responses. Arch Intern Med. 1968 Jul;122(1):6–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubenstein A. H., Cho S., Steiner D. F. Evidence for proinsulin in human urine and serum. Lancet. 1968 Jun 22;1(7556):1353–1355. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., BISHOP J. S., DUNN A., ALTSZULER N., RATHBEB I., DEBODO R. C. INHIBITION BY INSULIN OF HEPATIC GLUCOSE PRODUCTION IN THE NORMAL DOG. Am J Physiol. 1965 Feb;208:301–306. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELE R., WALL J. S., DE BODO R. C., ALTSZULER N. Measurement of size and turnover rate of body glucose pool by the isotope dilution method. Am J Physiol. 1956 Sep;187(1):15–24. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1956.187.1.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUTHERLAND E. W., CORI C. F. Effect of hyperglycemic-glycogenolytic factor and epinephrine on liver phosphorylase. J Biol Chem. 1951 Feb;188(2):531–543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seltzer H. S., Allen E. W., Herron A. L., Jr, Brennan M. T. Insulin secretion in response to glycemic stimulus: relation of delayed initial release to carbohydrate intolerance in mild diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1967 Mar;46(3):323–335. doi: 10.1172/JCI105534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. G., Benedetti A., Grodsky G. M., Karam J. H., Forsham P. H. Early phase of insulin release. Diabetes. 1968 Nov;17(11):684–692. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.11.684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeldner J. S., Gleason R. E., Williams R. F., Garcia M. J., Beardwood D. M., Marble A. Diminished serum insulin response to glucose in genetic prediabetic males with normal glucose tolerance. Diabetes. 1968 Jan;17(1):17–26. doi: 10.2337/diab.17.1.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinkamp R. C., Cohen N. L., Gaffey W. R., McKey T., Bron G., Siri W. E., Sargent T. W., Isaacs E. Measures of body fat and related factors in normal adults. II. A simple clinical method to estimate body fat and lean body mass. J Chronic Dis. 1965 Dec;18(12):1291–1307. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(65)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinkamp R. C., Cohen N. L., Siri W. E., Sargent T. W., Walsh H. E. Measures of body fat and related factors in normal adults. I. Introduction and methodology. J Chronic Dis. 1965 Dec;18(12):1279–1291. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(65)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalow R. S., Glick S. M., Roth J., Berson S. A. Plasma insulin and growth hormone levels in obesity and diabetes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Oct 8;131(1):357–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb34803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


